Figure 1.
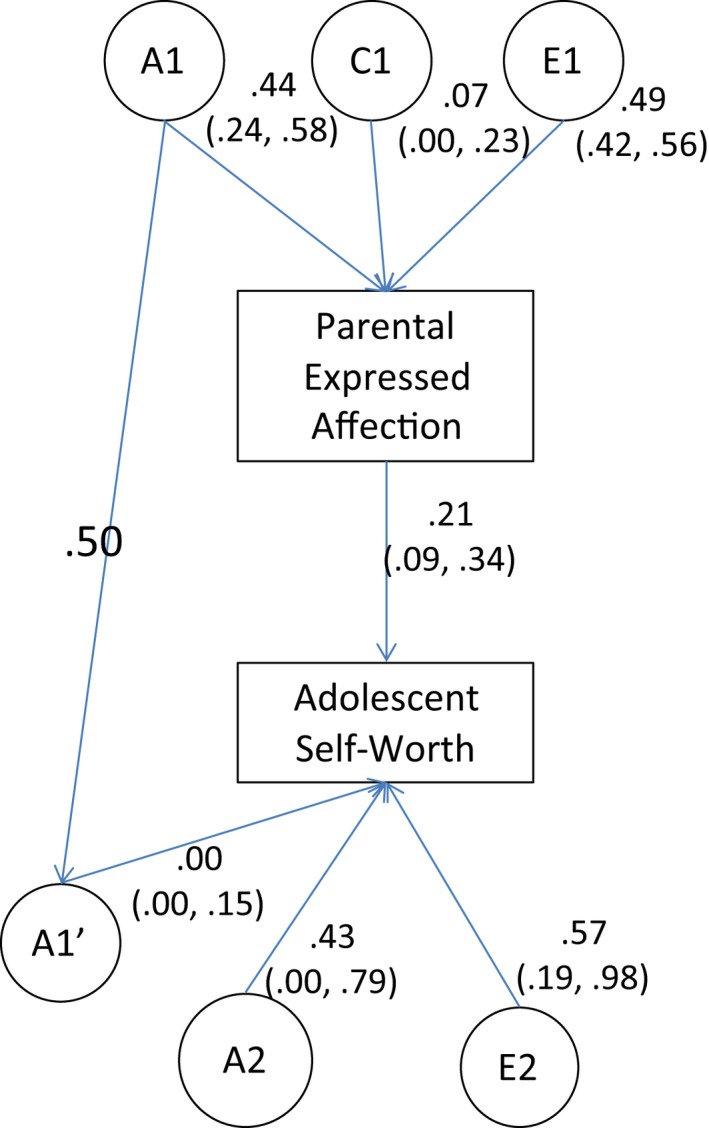
Structural equation models showing the association between parent‐reported affection within the parent–child relationship, and adolescent self‐worth. Path estimates are from the full (unconstrained) model in which all parameters are freely estimated. A1, Additive genetic effects on expressed affection; C1, shared environmental effects on expressed affection; E1, nonshared environmental effects on expressed affection; A1′, genetic effects common to parental expressed affection and adolescent self‐worth; A2, genetic effects specific to adolescent self‐worth; E2, nonshared environmental effects on adolescent self‐worth. The path between Parental Expressed Affection and Adolescent Self‐Worth is the phenotypic transmission pathway. NB, the pathway between A1 and A1′ is fixed to .50 because parents and children share 50% of their genome
