Table 1. Properties of real networks analyzed in this paper.
| Label | Name | N | E | 〈k〉 | 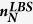 |
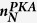 |
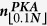 |
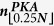 |
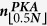 |
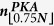 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neuronal | ||||||||||
| 1 | C. Elegans | 307 | 2657 | 8.6547 | 10 | 10 | 55 | 43 | 29 | 11 |
| 2 | Co-Activation | 638 | 37250 | 58.3856 | 1 | 1 | 11 | 5 | 3 | 2 |
| 3 | Macaque 71 | 71 | 746 | 10.5070 | 1 | 1 | 15 | 9 | 3 | 2 |
| Food Webs | ||||||||||
| 4 | Florida | 128 | 2106 | 16.4531 | 30 | 30 | 51 | 42 | 35 | 34 |
| 5 | Mondego | 46 | 400 | 8.6957 | 19 | 19 | 27 | 23 | 20 | 20 |
| 6 | St. Marks | 54 | 356 | 6.5926 | 13 | 13 | 23 | 19 | 15 | 15 |
| Trust | ||||||||||
| 7 | College | 32 | 96 | 3.0000 | 6 | 6 | 17 | 9 | 6 | 6 |
| 8 | Prisioners | 67 | 182 | 2.7164 | 9 | 11 | 24 | 20 | 14 | 14 |
| Transportation | ||||||||||
| 9 | US largest 500 airport | 500 | 2980 | 5.9600 | 281 | 281 | 291 | 286 | 282 | 281 |
| Intra-Orgazinational | ||||||||||
| 10 | Freemans (EIES-1) | 46 | 695 | 15.1087 | 12 | 13 | 23 | 16 | 14 | 14 |
| 11 | Freemans (EIES-3) | 32 | 460 | 14.3750 | 1 | 1 | 14 | 4 | 3 | 3 |
| Reg. and Metabolic | ||||||||||
| 12 | Ecoli | 99 | 212 | 2.1856 | 22 | 22 | 39 | 28 | 27 | 22 |
| Electric Circuit | ||||||||||
| 13 | s208 | 122 | 189 | 1.5492 | 29 | 29 | 47 | 33 | 30 | 30 |
| 14 | s420 | 252 | 399 | 1.5833 | 59 | 59 | 73 | 66 | 62 | 62 |
| 15 | s838 | 512 | 819 | 1.5996 | 119 | 119 | 140 | 128 | 125 | 123 |
| Protein | ||||||||||
| 16 | Protein 1 | 95 | 213 | 2.2421 | 18 | 18 | 33 | 24 | 21 | 19 |
| 17 | Protein 2 | 53 | 123 | 2.3208 | 13 | 13 | 23 | 18 | 14 | 14 |
| 18 | Protein 3 | 99 | 212 | 2.2316 | 22 | 22 | 39 | 28 | 27 | 22 |
Legend: n denotes the number of nodes, E denotes the number of directed edges, 〈k〉 denotes the average degree, 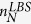 the number of driving nodes and
the number of driving nodes and 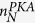 the number of driven nodes to ensure structural controllability, and
the number of driven nodes to ensure structural controllability, and 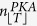 the number of driven nodes required if the structural controllability index is set to be equal to
the number of driven nodes required if the structural controllability index is set to be equal to 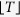 , with T = 0.1N, 0.25N, 0.5N, 0.75N.
, with T = 0.1N, 0.25N, 0.5N, 0.75N.
