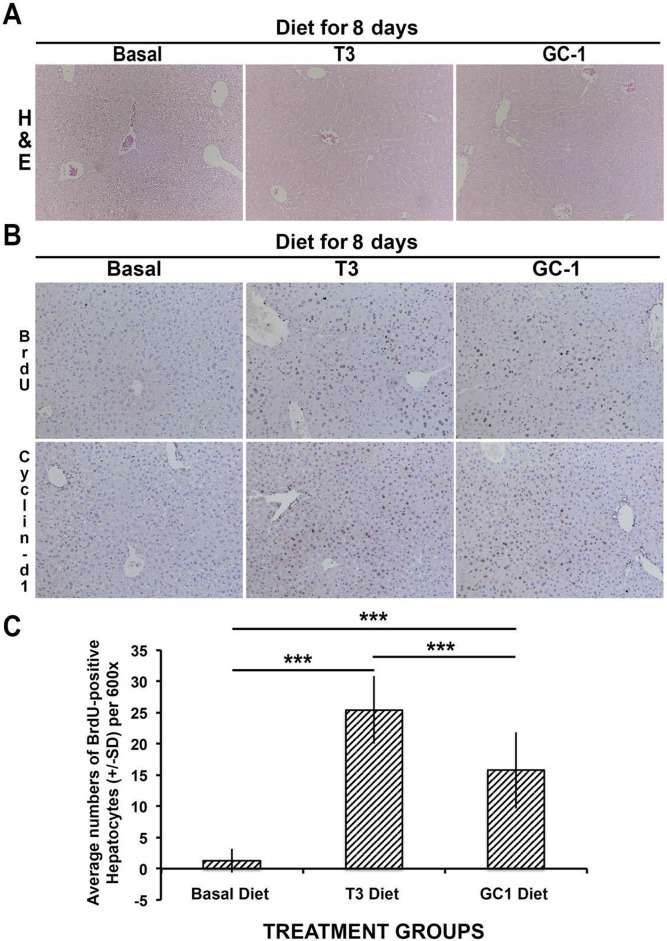
Figure 3.
Increased hepatocyte proliferation in wild-type mice fed T3-supplemented (4 mg/kg) and GC-1-supplemented (5 mg/kg) diets. (A) Similar hepatic histology is observed in H&E-stained sections in basal diet-, T3 diet-, and GC diet-fed mice as shown in representative images from all three groups (100×). (B) Immunohistochemistry shows increased BrdU incorporation and increased nuclear cyclin D1 in both T3 diet- and GC-1 diet-fed groups when compared to basal diet-fed animals (100×). (C) Bar graphs showing average number of BrdU-positive hepatocyte nuclei per HPF (600×) in different conditions. Ten HPFs were counted for each group. T3- and GC-1-fed animals had significantly more BrdU-positive hepatocyte nuclei than basal diet GC-1-fed mice (***p < 0.001). Interestingly, a significant difference in hepatocyte proliferation was also evident between the T3 diet- and GC-1-diet fed mice (***p < 0.001).