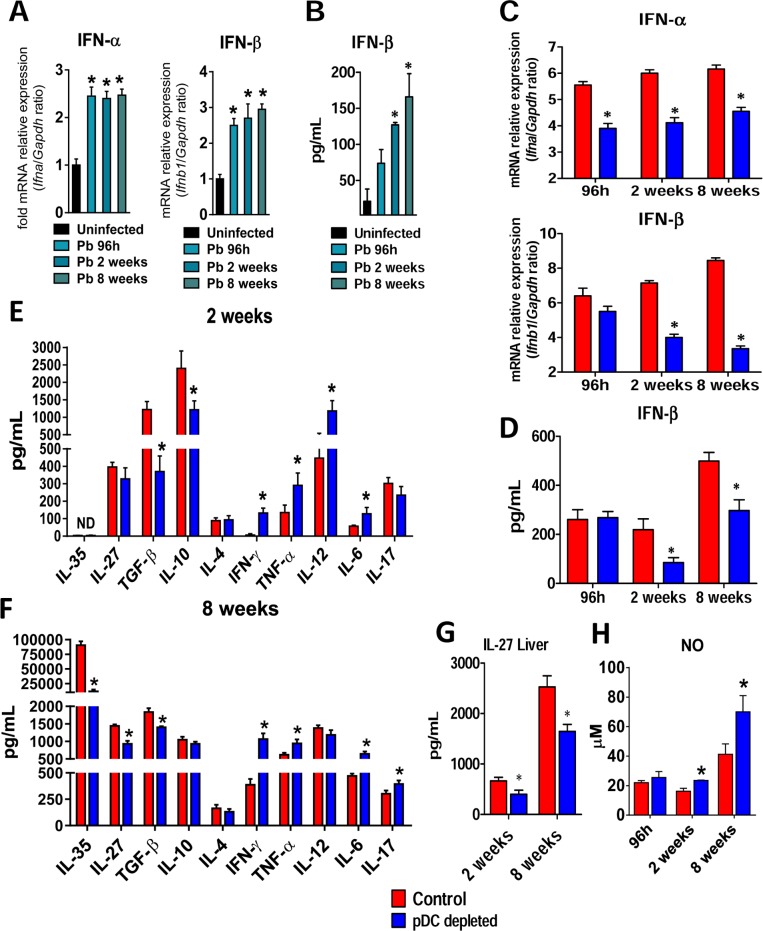
Fig 3. pDC-depletion reduces the mRNA expression of type I IFNs, secreted IFN-β and anti-inflammatory cytokines but increases the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
(A) Expression of IFN-α and IFN- β mRNA in the lungs of uninfected or P. brasiliensis infected mice after 96 h, 2 and 8 weeks of infection. (B) Type I IFN quantitation by ELISA in lung homogenates from uninfected and infected mice at the same post-infection periods. (C) mRNA relative expression of IFN-α and IFN- β in the lungs of anti-PDCA or control isotype mAb treated mice. (D) Type I IFN quantitation by ELISA in lung homogenates from pDC-depleted or control mice. (E-F) Cytokines quantitation by ELISA in lung homogenates from pDC-depleted or control mice at weeks 2 and 8 after infection. (G) IL-27 quantitation by ELISA in liver homogenates from pDC-depleted or control mice. (H) Supernatants of lung homogenates were also used to determine the levels of nitrite by the Griess reagent. Bars show mean ± SD from at least four mice per group and are representative of two independent experiments (*p< 0.05).