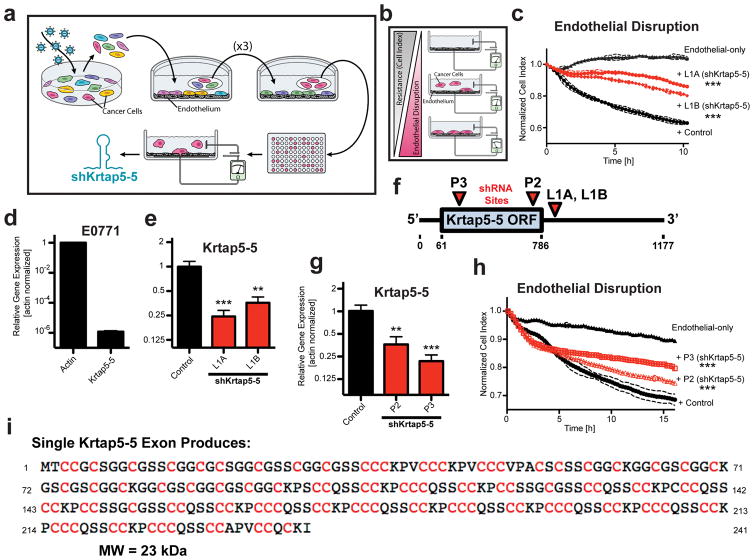
Figure 1.
Genome-wide RNAi screen implicates Krtap5-5 in cancer cell interaction with an endothelial monolayer. (a) Schematic of RNAi screen. E0771 transduced with a genome-wide RNAi library were subjected to Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cell (HUVEC) monolayer attachment. Unattached cells were collected and expanded over three rounds. After the 4th round, clonal cells were generated by limiting dilution and tested functionally, and the inserted shRNA was identified by sequencing. (b) Electric Cell-substrate Impedance Sensing (ECIS) monitors real-time disruption of an endothelial monolayer by invading cancer cells10. (c) Clonal E0771 lines derived from the RNAi library screen (L1A, L1B) show reduced endothelial monolayer disruption relative to control cells with a non-silencing shRNA. The plot depicts real-time disruption of endothelial monolayer after addition of cancer cells (data point intervals, 15 min). *** p<0.001, vs control; mean ± SD. (d) Expression of Krtap5-5 mRNA in E0771 cells relative to actin. Mean ± SEM. (e) Krtap5-5 mRNA in RNAi library screen-derived L1A and L1B cells. ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001, vs controls; mean ± SEM. (f) shRNA targeting sites relative to the Krtap5-5 mRNA. P2, P3 shRNAs were used to generate de novo pooled knockdown cell lines. ORF = open reading frame. (g) Krtap5-5 mRNA in P2 and P3 cells. ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001, vs controls; mean ± SEM. (h) P2 and P3 cell disruption of an endothelial monolayer as in panel c. *** p<0.001, mean ± SD. (i) Krtap5-5 amino acid sequence highlighting cysteine residues.