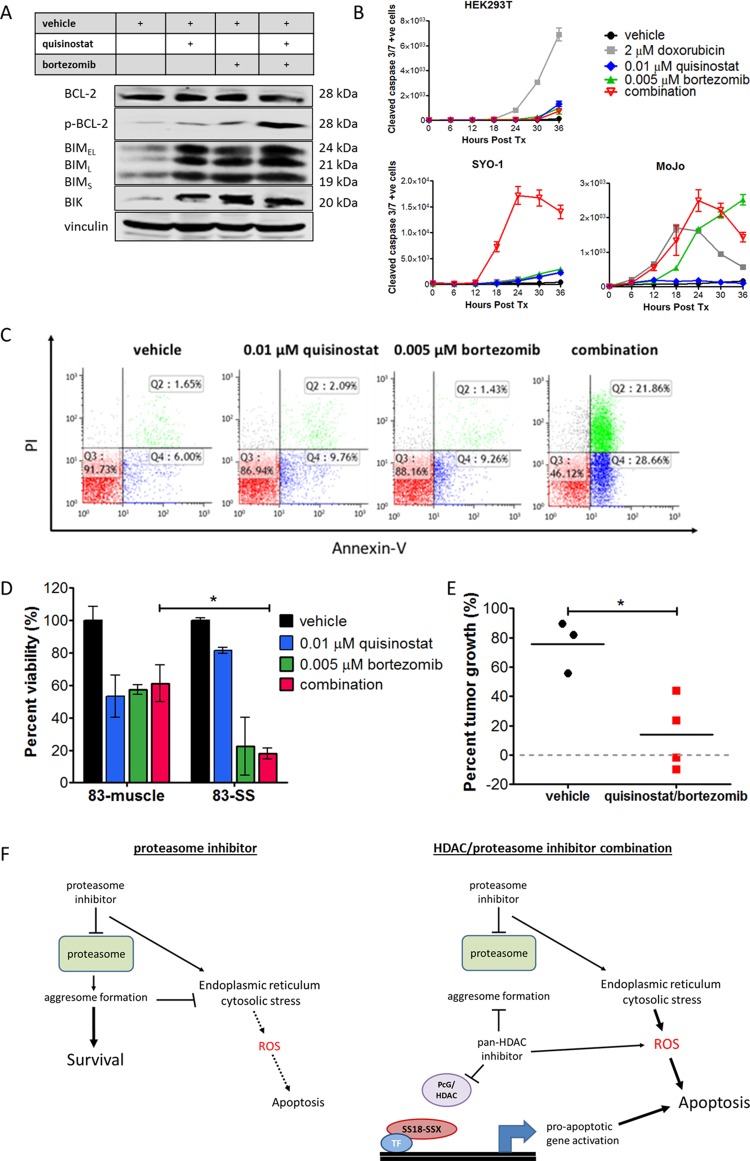
Fig 6. HDAC and proteasome inhibition leads to apoptosis via pro-apoptosis protein activation, ROS production and caspase activation.
(A) Pro-apoptotic proteins BIM and BIK are upregulated by both quisinostat and bortezomib, and the drug combination elicits phosphorylation of anti-apoptotic protein BCL-2 in SYO-1 cells. (B) Cleavage of caspase 3 occurs following treatment with the drug combination in synovial sarcoma cell lines, demonstrated by staining with IncuCyte™ Kinetic Caspase-3/7 Apoptosis Assay Reagent, (C) inducing significant apoptosis as confirmed by Annexin-V/PI staining in the SYO-1 cell line (Q3: live, Q2: necrotic/late apoptotic, Q4: early apoptotic). (D) The low-dose quisinostat/bortezomib drug combination brings about a significant decrease in the viability of primary synovial sarcoma cells (83-SS) as compared to matched normal muscle cells derived from the same patient (83-muscle). Two-way ANOVA indicated a significant interaction between cell type and response to the drug combination (p < 0.05). (E) Tumor growth in a murine model of synovial sarcoma was significantly reduced by day 21 with the quisinostat/bortezomib combination treatment, as compared to the vehicle only control. (F) Taken together, the combination of HDAC and proteasome inhibitors results in dissociation of the SS18-SSX driving complex as well as aggresome inhibition, ER stress and ROS production, leading to apoptosis induction in synovial sarcoma. Statistical significance compared to vehicle treatment controls was determined by Student t test or two-way ANOVA where indicated: * denotes p < 0.05. Error bars represent standard error of mean from conditions performed in triplicate. Vinculin was used as a loading control for protein analysis.