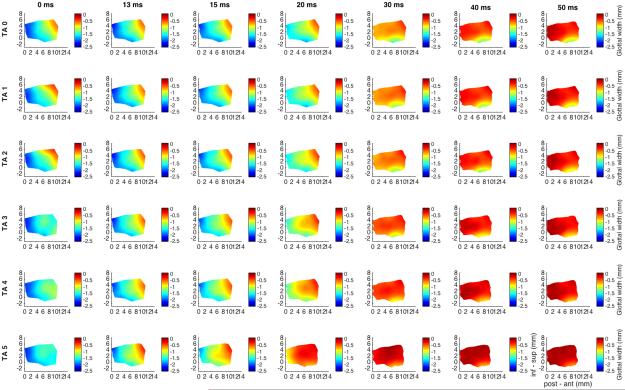
Fig. 2.
Glottal shape for the interaction between maximal LCA activation and graded TA activation. Design layout is same as Fig.1 except now LCA is held at maximum stimulation for all rows (grade 6), while TA is added in a graded fashion from grade 0 (‘TA 0’, row 1) to grade 5 (‘TA 5’, row 6). Increased adduction is apparent as early as 13 ms for TA stimulation grade 3 and above. TA increases overall mid-point adduction from 82% with LCA alone to 95% with full TA grade 5 activation. LCA alone (row 1) results in 3.5% vocal fold shortening and a 4-7% vertical height narrowing. Added TA shifts vertical height thickening to the mid-to-anterior vocal fold with increased grade of activation. (inf – sup = inferior to superior, LCA = lateral cricoarytenoid, ms = millisecond, post – ant = posterior to anterior, TA = thyroarytenoid).