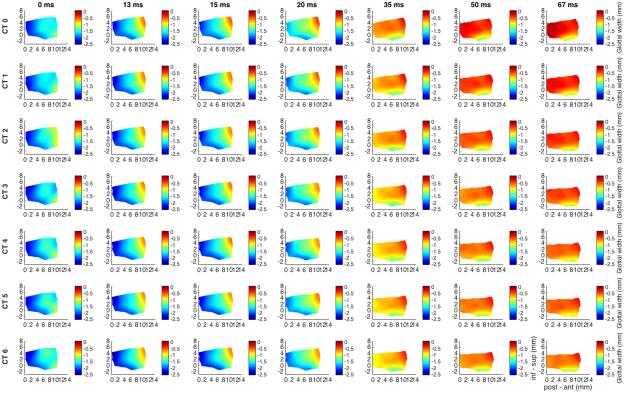
Fig. 8.
Glottal shape for the interaction between maximal LCA activation and graded CT activation. Design layout is same as Fig.1 except now LCA is held at maximum stimulation for all rows (grade 6), while CT is added in a graded fashion from grade 0 (‘CT 0’, row 1) to grade 6 (‘CT 6’, row 7). The LCA itself does not change the length of the vocal fold, however with increasing CT activation the vocal fold is lengthened up to 7%. LCA alone (row 1) causes 88% adduction which is reduced by 25% (to 63%) with full grade 6 CT activation. LCA results in vertical thickness thinning by 5-7%. This thinning is further augmented by CT activation to 19%. Again, CT activation helps distribute the posterosuperior effect of LCA more evenly along the glottal axis. (CT = cricothyroid, inf – sup = inferior to superior, LCA = lateral cricoarytenoid, ms = millisecond, post – ant = posterior to anterior).