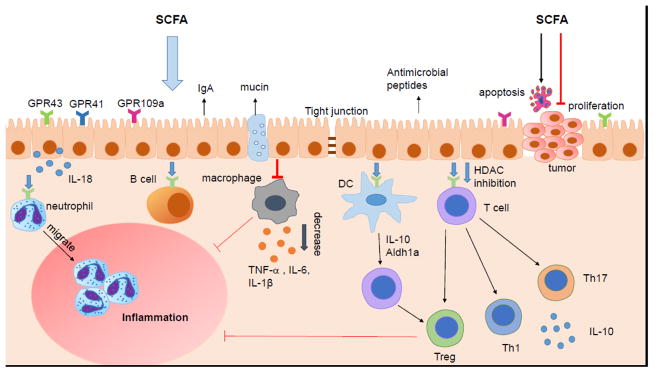
Figure 2. SCFA regulation of intestinal immunity.
SCFA regulate the intestinal mucosal immunity through exerting their effects on various immune cells. SCFA regulate intestinal barrier integrity by inducing intestinal epithelial cell secretion of IL-18, antimicrobial peptides, mucin, and upregulating the expression of tight junction. SCFA induce neutrophils migration to inflammatory site and enhance their ability of phagocytosis. SCFA regulate the T cell function not only through GPCR pathway but also inhibition of HDAC. The differentiation of T cell is mediated both by SCFA regulation of DC and the direct act of SCFA on T cells. SCFA regulate the generation of Th1, Th17 and Treg in different cytokine milieu. SCFA also inhibit intestinal macrophage production of proinflamamtory cytokines through inhibition of HDAC, and possibly induce intestinal IgA production of B cells. Moreover, SCFAs inhibit the carcinogenesis through promoting apoptosis and suppressing proliferation of tumor cells.