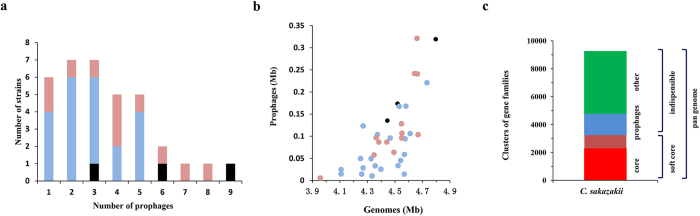
Figure 1. Impact of prophages on genetic diversity of Cronobacter sakazakii.
(A) Frequencies of integrated prophages in the genomes of C. sakazakii strains. The strains isolated from clinical sample, food and environmental sample were colored with light red, light blue and black, respectively. (B) Correlation between genomic sizes of C. sakazakii and prophages. There was a significant positive correlation between the genome sizes of C. sakazakii strains and integrated prophages (Spearman’s ρ = 0.74, P < 10−4). The strains were colored the same as in Fig. 1A. (C) Contribution of prophage genes to genomic composition of C. sakazakii. The core genome corresponds to genes present in all strains, whereas the soft-core genome indicates genes present in more than 95% of the strains. The indispensable genome was split into two categories: prophages and other genes.