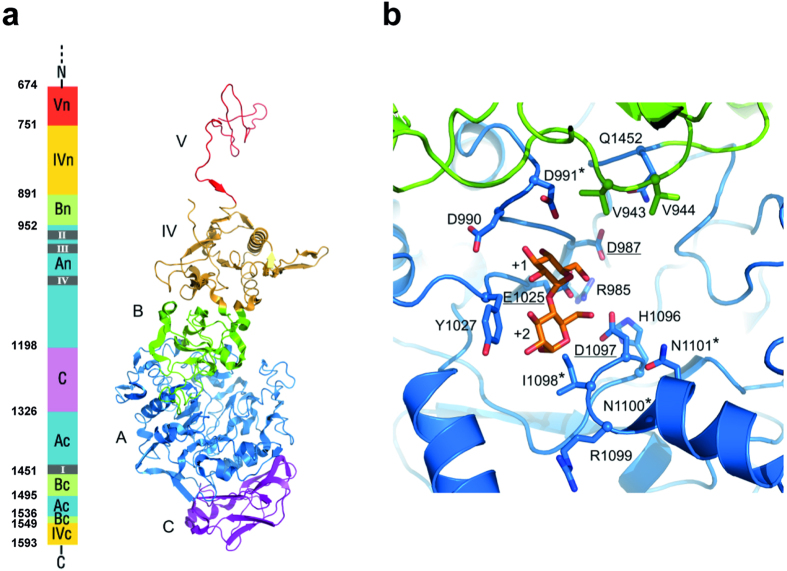
Figure 2. Homology model for L. fermentum NCC 2970 GtfB.
Tertiary structure prediction was accomplished by using the Phyre2 server37. Among the different templates found, the L. reuteri 180 Gtf180-ΔN (PDB: 3KLK20), was chosen as it displayed the highest homology with L. fermentum NCC 2970 GtfB in domains A and B. (a) Schematic representation of the L. fermentum GtfB 3D model structure. Domains A, B, C, IV and V are colored in blue, green, magenta, yellow and red, respectively. Only part of the N-terminal half of domain V is present in the homology model. (b) Close-up of the active site at the interface of domains A (blue) and B (green). The catalytic residues (underlined) and other residues lining the active site, present in motifs I-IV are shown in stick representation. Residues that are different from previously identified 4,6-α-GTases are indicated with an asterisk. A maltose acceptor substrate bound in subsites +1 and +2 (orange carbon atoms) is shown based on the Gtf180/maltose complex (PDB: 3KLL20).