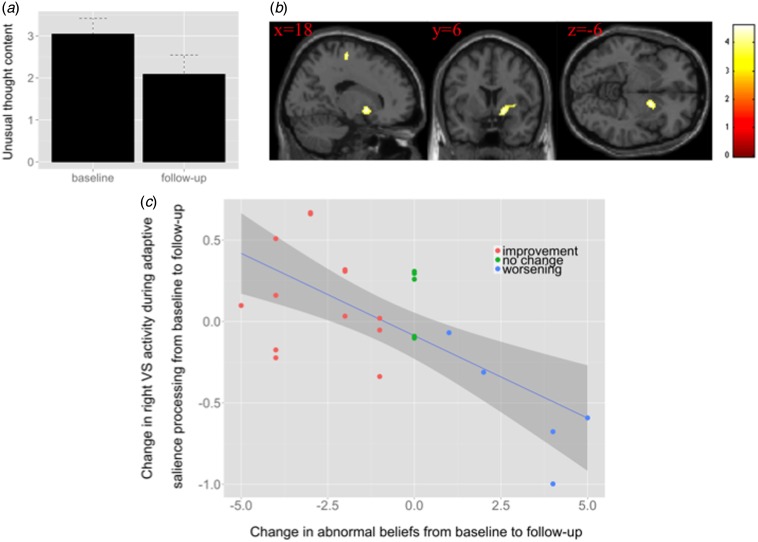
Fig. 4.
(a) Unusual thought content (abnormal beliefs) at baseline (mean: 3.04) and follow-up (mean: 2.09) in ultra-high-risk (UHR) subjects (t22 = 1.775, p = 0.09). (b) Negative correlation between changes in brain activation during adaptive reward prediction and changes in abnormal beliefs from baseline to follow-up in UHR subjects. The image is displayed at a cluster-forming threshold of p < 0.001 uncorrected, with an extent threshold of 20 voxels. The colour bar indicates t values. (c) Scatterplot of negative relationship between change in right ventral striatum (VS) activation during adaptive salience processing, taken from the peak voxel in (b) and change in abnormal beliefs [Comprehensive Assessment of At-Risk Mental States (CAARMS) item unusual thought content] from baseline to follow-up in UHR subjects (r = −0.702).