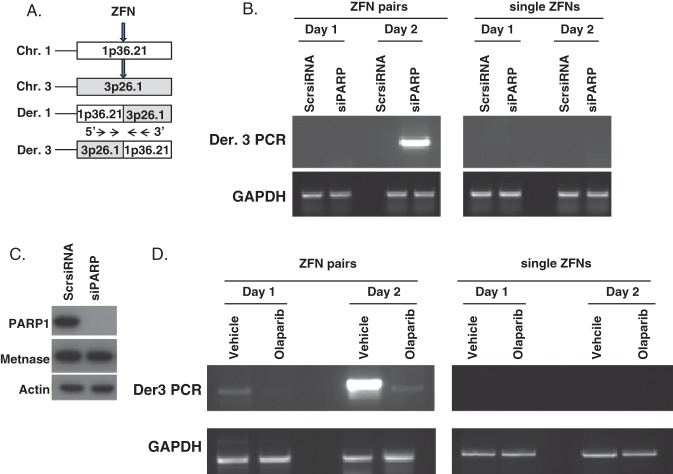
Fig. 1.
Olaparib inhibition of polyadenosine diphosphate ribose polymerase 1 (PARP1) or PARP1 small interfering RNA (siRNA) decrease zinc finger nuclease-induced translocations. (A) Olaparib-treated HEK-293T cells transfected with siRNA and zinc finger nucleases (ZFN) to induce double-strand breaks (DSBs) for a 1;3 translocation at the times indicated. (B) PARP1 siRNA repressed ZFN-induced translocations, as assayed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of the der[3] product. Translocations are only generated by two ZFN pairs, required to create two simultaneous DSBs in target chromosomes, but not by the negative control single ZFNs of each pair. That siRNA against PARP1 represses translocations indicates that the translocation effect is specific to PARP1 inhibition, and not an off-target effect of olaparib. (C) siRNA against PARP1 represses the expression of PARP1 protein, but has no effect on Metnase protein, indicating its specificity. (D) Quantification of ZFN–induced translocations with or without olaparib using PCR to detect the der[3] translocation product. These data raise the possibility that oncogenic translocations can be prevented in high risk situations by treatment with the clinical PARP1 inhibitors. From Wray et al (92); used by permission. Abbreviations: Chr, Chromosome; Der, Derivative; Scr, Scrambled; GAPDH, Glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase.