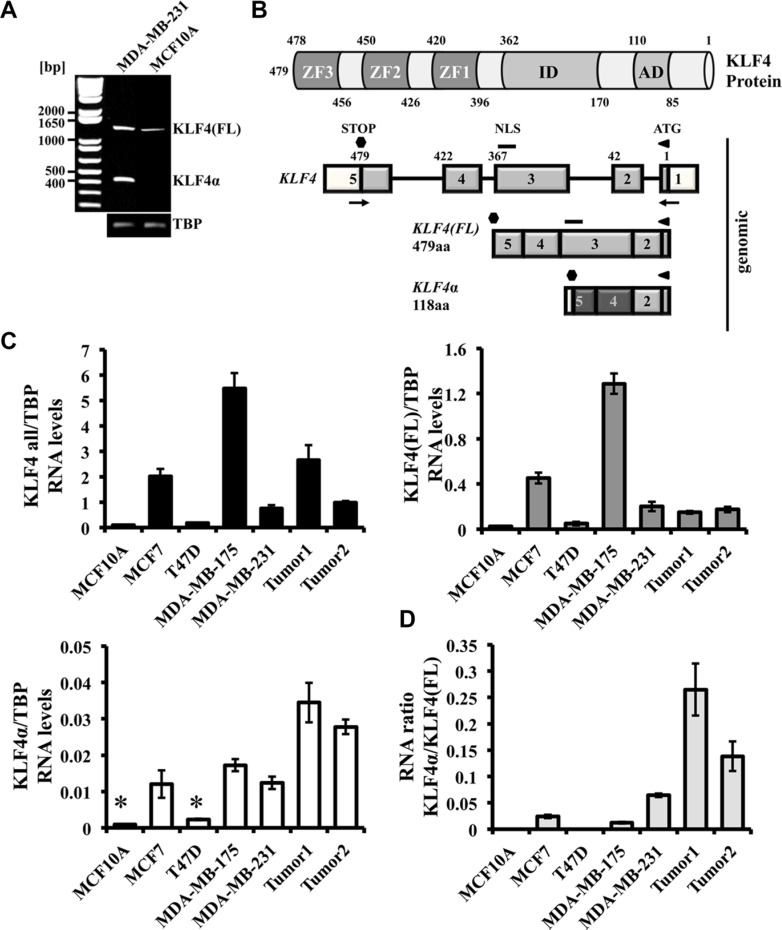
Figure 1. Detection of KLF4α in human breast cancer cells.
(A) RT-PCR analysis of KLF4 in MDA-MB-231 and MCF10A cells. Both cell lines show the KLF4(FL) band (∼1440 bp), whereas the KLF4α band (∼440 bp) is only detectable in MDA-MB-231 cells. (B) Schematic representation of the KLF4 protein structure (top) and the KLF4 gene and its variants in MDA-MB-231 cells (bottom). The KLF4 gene is located on chromosome 9 (reverse strand), contains 5 exons, which gives rise to a KLF4(FL) protein of 479aa. Skipping of exon3 produces KLF4α (118aa). Numbers indicate the amino acids. AD: activation domain; ID: inhibitory domain, ZF: zinc fingers; NLS: nuclear localization signal; aa: amino acids; white boxes: untranslated exons; light grey boxes: shared sequence between KLF4(FL) and KLFα; dark grey boxes: novel sequence in KLF4α; arrows: primers used in A). (C) qPCR analysis of a normal human breast cell line (MCF10A) compared to four human breast cancer cell lines and two human ductal breast carcinoma patients for the genes KLF4 all, KLF4(FL), and KLF4α. Note that KLF4α is detectable in three out of the four breast cancer cell lines and that the two breast cancer patient samples show high levels of KLF4α compared to cells. Data are expressed as the mean +/− SEM. n = 3. TBP: TATA-Box binding protein. *CT values ≥ 34. (D) RNA ratio of KLF4α/KLF4(FL) indicates highest ratio in the two cancer patient samples.