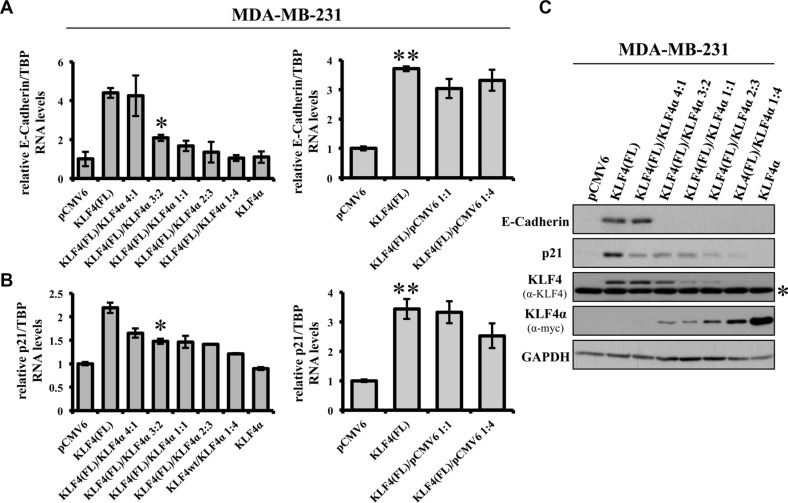
Figure 5. KLF4α antagonizes KLF4(FL)-mediated effects on E-Cadherin and p21.
(A) MDA-MB-231 cells were transiently transfected with different ratios of KLF4α and KLF4(FL) followed by qPCR analysis for E-Cadherin. Increasing amounts of KLF4α block KLF4(FL)-mediated E-Cadherin RNA induction (left panel). As a control, different ratios KLF4(FL)/pCMV6 were used followed by qPCR for E-Cadherin levels. Note that even KLF4(FL)/pCMV6 ratio of 1:4 still robustly induced E-Cadherin (right panel). Data are expressed as the mean +/− SEM. n = 3. *p ≤ 0.05 (KLF4(FL) versus (FL)/α 3:2). **p ≤ 0.05 (KLF4(FL) versus pCMV6). (B) KLF4α/KLF4(FL) imbalance in MDA-MB-231 cells reduces KLF4(FL)-provoked p21Cip1 induction as evidenced by qPCR (left panel). Right panel shows the control using different KLF4(FL)/pCMV6 ratios. Data are expressed as the mean +/− SEM. n = 3. TBP: TATA-Box binding protein. *p ≤ 0.05 (KLF4(FL) versus (FL)/α 3:2). **p ≤ 0.05 (KLF4(FL) versus pCMV6). (C) MDA-MB-231 cells were transiently transfected with different ratios of KLF4α and KLF4(FL) followed by immunoblot analysis using specific antibodies for E-Cadherin and p21Cip1. Note that KLF4α/KLF4(FL) imbalances are reflected on protein levels as assessed by anti-KLF4 (KLF4(FL)) and anti-myc (KLF4α) and abrogate E-Cadherin and p21Cip1 inductions. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. *background band.