Figure 5. ODE activates p53 signaling in CRC cells.
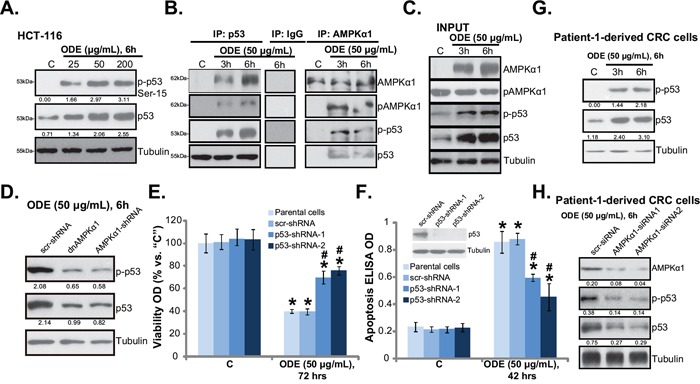
HCT-116 cells were treated with or without ODE at applied concentrations, cells were further cultured, expressions of listed proteins were tested by Western blots A and C., the association between AMPKα1 (regular and p-) and p53 (regular and p-) was examined by co-immunoprecipitation (“Co-IP”) assay B., IgG was also included as a Co-IP control (B). Stable HCT-116 cells expressing scramble-shRNA (“scr-shRNA”), AMPKα1-shRNA or dominant negative (dn)-AMPKα1 (“dnAMPKα1”) were treated with applied ODE, p53 (regular and p-) and Tubulin expressions were tested by Western blots D. Stable HCT-116 cells expressing scramble-shRNA (“scr-shRNA”) or p53-shRNA (“−1/−-2”) as well as their parental cells were treated with applied ODE, cell viability (MTT assay, E.) and cell apoptosis (Histone DNA ELISA assay, F.) were tested, expression of p53 in these cells was also shown (F, upper panel). p53 (regular and p-) and Tubulin expressions in ODE (50 μg/mL)-treated primary CRC cells (patient-1 derived) were shown G. p53 (regular and p-) and AMPKα1 expressions in ODE (50 μg/mL)-treated primary CRC cells with scramble control siRNA (“scr-siRNA”) or AMPKα1 siRNA (“−1/−2”) were shown H. Kinase phosphorylations and p53 expression were quantified. Data in this figure were repeated three times, and similar results were obtained. * p < 0.05 vs. “C” of “scr-shRNA” group. # p < 0.05 vs. “ODE” of “scr-shRNA” group.
