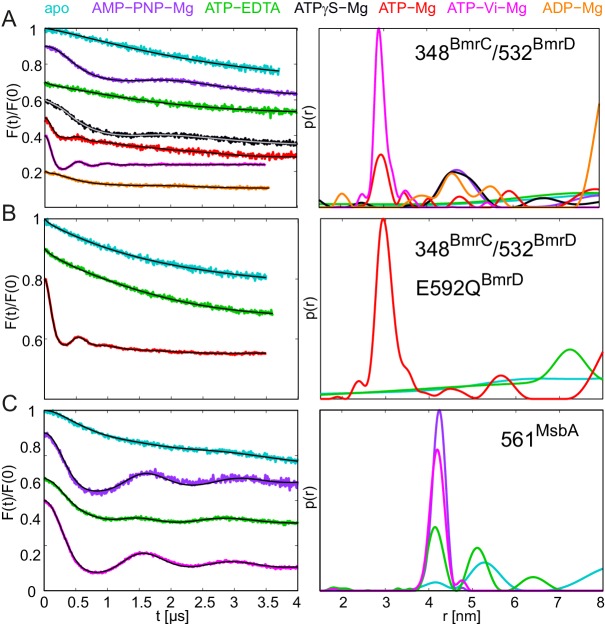
Figure 9. DEER analysis of spin-labeled pairs in the NBDs of BmrCD and MsbA.
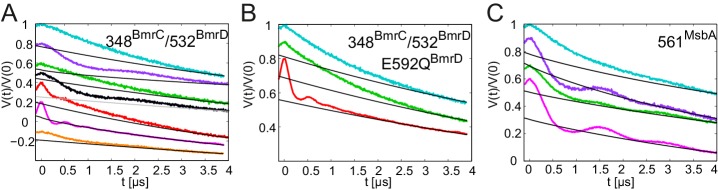
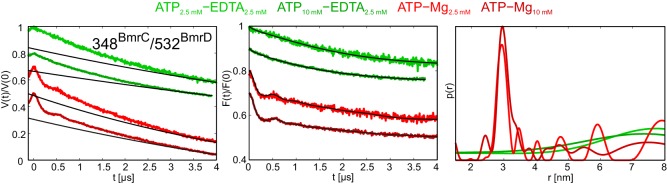
Q-band background-corrected DEER traces [F(t)/F(0)] with fitted distribution function (left) and corresponding distance distribution (right). (A) Spin labeled pair 348BmrC/532BmrD in wildtype BmrCD and (B) in BmrCD carrying the E-to-Q substitution incubated with different nucleotides and nucleotide analogs. (C) Spin labeled 561MsbA in wildtype MsbA incubated with different nucleotides and nucleotide analogs. Primary DEER traces are shown in Figure 9—figure supplement 1. DEER traces detected for BmrCD after incubation with 10 mM nucleotides are shown in Figure 9—figure supplement 2.