Figure 1.
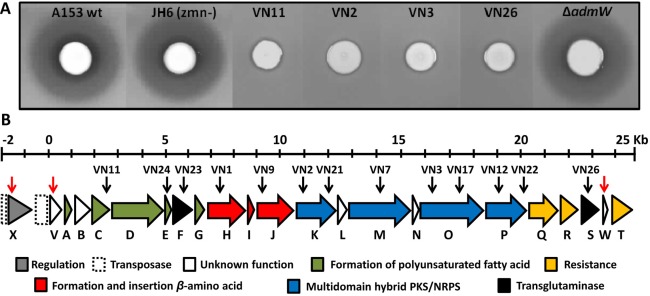
Identification and characterization of the andrimid gene cluster in Serratia plymuthica A153.
A. Antibacterial activities against Bacillus subtilis of Serratia plymuthica A153, and derivative strains with mutations in the zeamine (zmn) and andrimid (adm) biosynthetic gene clusters.
B. Genetic organization of the adm gene cluster in S. plymuthica A153. The same genetic organization was found in S. marcescens MSU97 and S. marcescens 90‐166 (Fig. S3). Location of the Tn‐KRCPN1 transposon insertions and in‐frame deletion mutants are indicated by black and red arrows, respectively. Colour code representing the functional category of each gene of the gene cluster is given where possible, based on the biosynthetic pathway for andrimid proposed by Jin et al. (2006). Genes admV, admW and admX were not previously associated with the regulation or biosynthesis of andrimid.
