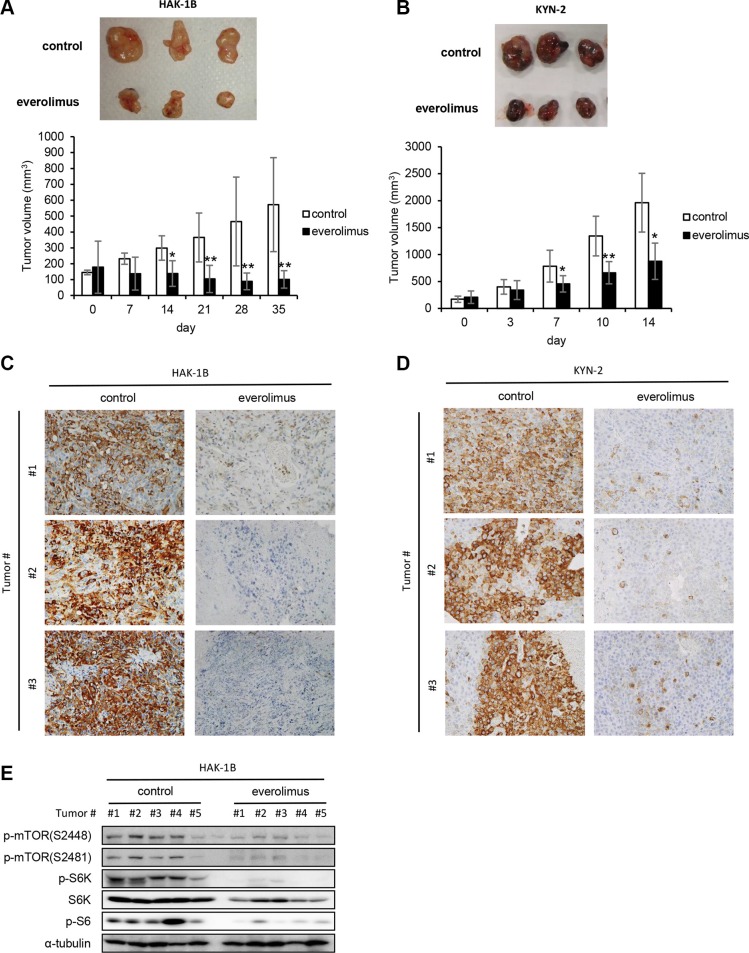
Figure 5. Effect of everolimus on tumor growth and activation of mTOR-related signaling molecules in vivo.
(A, B) Antitumor effects of everolimus on the growth of HAK-1B (A) and KYN-2 (B) xenografts. Mice were inoculated subcutaneously with HCC cells, and mice with tumors >100 mm3 were treated orally with everolimus (2 mg/kg/day) or a control CMC daily from day 0 until days 35 or 14 (n = 5 mice per each group). Each bar is the average ± SD, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 (two-tailed Student t test). (C, D) Effects of everolimus on S6 phosphorylation in tumors formed by HAK-1B (C) or KYN-2 (D) cells analyzed on days 35 or 14 using immunohistochemistry with an anti-p-S6 antibody. Three tumors of the control and treated groups are shown. (original magnification ×100) (E) Inhibitory effects of everolimus on the activation of mTOR-related signaling molecules in tumors. Western blot analysis of the expression of phosphorylated mTOR, S6K, and S6 in five tumors treated with or without everolimus in vivo. α-tubulin served as loading control.