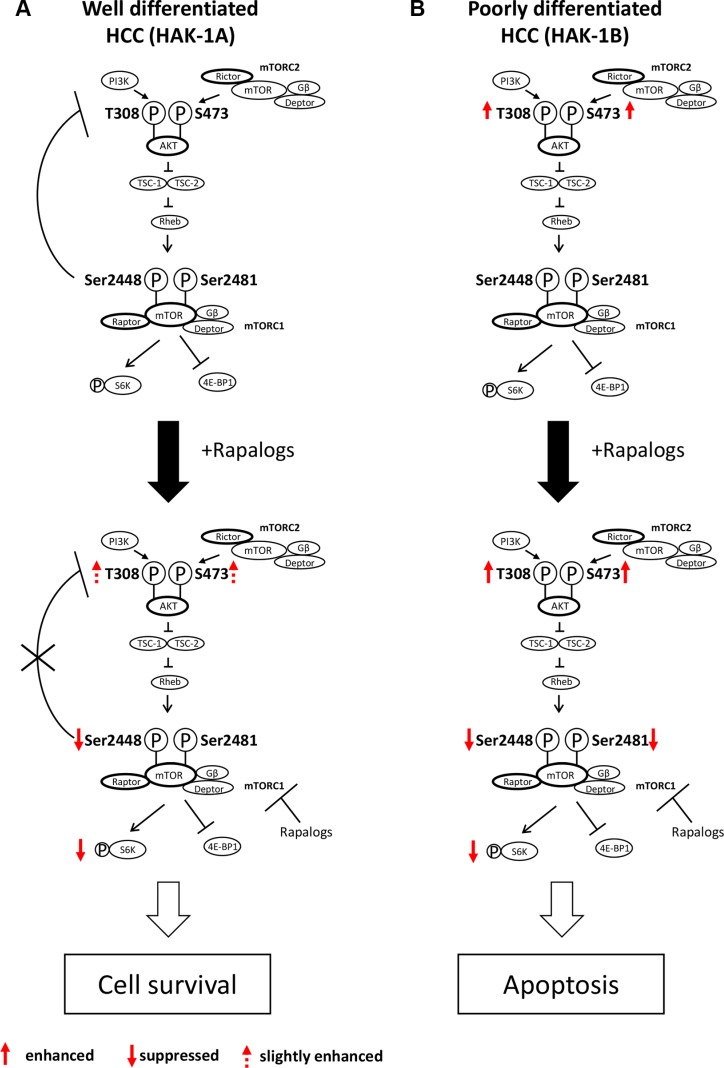
Figure 6. Hypothetical model of the acquisition of hypersensitivity to rapalogs by HCC cells.
(A) Normally, PI3K/AKT activation is under feedback regulation by mTORC1/S6K, such as in well differentiated HCC cells (e.g. HAK-1A cells). Rapalogs inhibit feedback suppression by mTORC1/S6K, possibly through drug-induced inhibition of the phosphorylation of mTOR Ser2448, which is accompanied by PI3K/AKT activation. Rapalogs do not affect the phosphorylation mTOR Ser2481 (mTORC1 complex), and the cells survive in the presence of drugs. (B) In contrast, PI3K/AKT is constitutively activated in poorly differentiated HCC cells (e.g. HAK-1B cells), and feedback control of PI3K/AKT by mTORC1 is dysregulated in this cell line. Rapalogs block the phosphorylation of both mTORC1 Ser2448 and Ser2481 that induces the death of HAK-1B cells through suppression of mTORC1-dependent cell growth, survival, and metabolism.