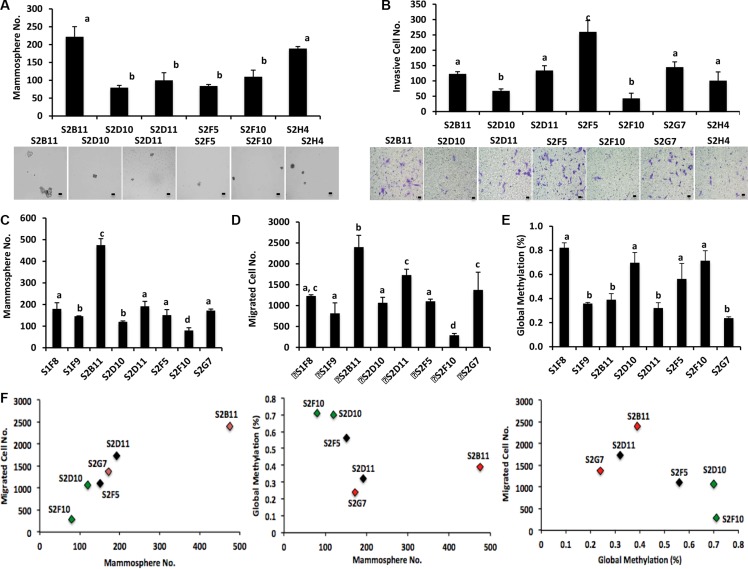
Figure 2. Different mammosphere formation ability and DNA methylation in CD49f+/CD44+/CD24− single-cell derived clones.
(A) Mammosphere formation was evaluated in different clones that were derived from CD49f+/CD44+/CD24− single cells. Clones showed a big variation in terms of their mammosphere forming capacity. Bar scale represents 50 μm. One-way ANOVA is used to perform the correlation analysis. Samples with no statistically significant differences are placed in the same letter group. Differentiated groups have at least a p value of less than 0.05. (F stat = 25.61; p value = 0.0006; df = 5). (B) The ability of the CD49f+/CD44+/CD24− single cell derived clones to invade was assessed via transwell invasion assay. The clones showed a variation in terms of their invading capacity and the invasion pattern of the clones matched their mammosphere formation ability. Bar scale represents 25 μm. One-way ANOVA is used to perform the correlation analysis. Samples with no statistically significant differences are placed in the same letter group. Differentiated groups have at least a p value of less than 0.05. (F stat = 67.05; p value = 1.3e-12; df = 6). (C) Mammosphere formation ability of CD49f+/CD44+/CD24− single cell derived clones was compared to the mammosphere formation ability of CD49f+/CD24− single cell derived clones. CD49f+/CD44+/CD24− single cell derived clones formed more and bigger mammospheres compared to most aggressive CD49f+/CD24− single cell derived clones. One-way ANOVA is used to perform the correlation analysis. Samples with no statistically significant differences are placed in the same letter group. Differentiated groups have at least a p value of less than 0.05. (F stat = 75.92; p value = 1.1e-06; df = 7) (D) The migration capacity of CD49f+/CD44+/CD24− single cell derived clones was compared to the migration capacity of CD49f+/CD24− single cell derived clones. CD49f+/CD44+/CD24− single cell derived clones migrated more compared to most aggressive CD49f+/CD24− single cell derived clones. One-way ANOVA is used to perform the correlation analysis. Samples with no statistically significant differences are placed in the same letter group. Differentiated groups have at least a p value of less than 0.05. (F stat = 34.43; p value = 5.1e-11; df = 7). (E) Global DNA methylation status of CD49f+/CD44+/CD24− single cell derived clones was compared to the global methylation status of CD49f+/CD24− single cell derived clones. The clones showed a variation in terms of their global DNA methylation status but in general more aggressive clones had a lower global DNA methylation compared to less aggressive clones. One-way ANOVA is used to perform the correlation analysis. Samples with no statistically significant differences are placed in the same letter group. Differentiated groups have at least a p value of less than 0.05. (F stat =12.35; p value = 1.3e-06; df = 7). (F) Corelation analyses show a strong correlation between mammosphere formation ability and migration capacity of CD49f+/CD44+/CD24− single cell derived clones (R2 = 0.9, p < 0.01). The correlation coefficient is still on the positive side but not significant for the relationship between global methylation of these clones and their mammosphere formation and migration capacity (R2 = 0.4 and R2 = 0.5, respectively).