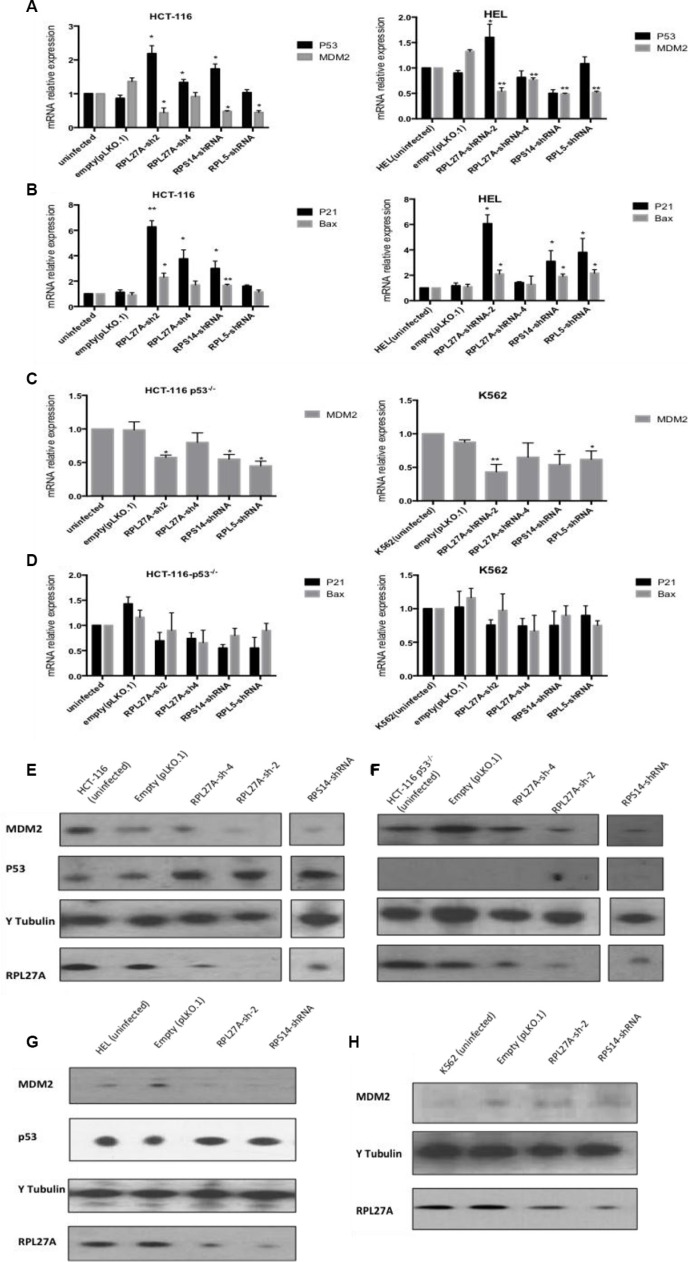
Figure 3. Decreased expression of RPL27A activates the p53 pathway.
HCT-116 and HEL cell lines dually express MDM2 and p53 mRNA. RPL27A and RPS14 depletion significantly augmented expression of p53 mRNA in HCT-116 cells compared to controls. RPL27A-sh2RNA, RPS14-shRNA and RPL5-shRNA reduced MDM2 expression in both cell lines (A). Increased expression of the p53 target genes p21 and Bax was induced by RPL27A and RPS14 depletion in HCT-116 and HEL cells (B). In the HCT116 p53−/− and K562 cell lines, MDM2 expression was reduced following RPL27A-shRNA2, RPS14-shRNA and RPL5-shRNA infection but no significant effects were noted for p21 or Bax expression. Bars display the mean results from three independent experiments ± SEM (p values were determined using two tail student t-test *p = < 0.05; **p = < 0.005)) (C, D). Protein expression of p53, MDM2 and RPL27A was determined following RPL27A-sh2 or RPS14-shRNA mediated knockdown. Tubulin was used as a loading control. In the HCT-116 and cell lines, depletion of RPL27A and RPS14 induced p53 expression and reduced MDM2 (E, G). In the HCT-116 p53−/− cell line, depletion of RPL27A and RPS14 reduced MDM2 expression (F). No significant reduction in MDM2 protein expression was identified compared to empty vector following infection with either RPL27A shRNA and RPS14 shRNA in K562 cells (H). In all cell lines, infection with RPS14 shRNA, caused a reduction in RPL27A expression. Results are representative of 3 independent experiments.