Figure 1. How KIFC1 drives tumor malignancy and prevents cancer cell death.
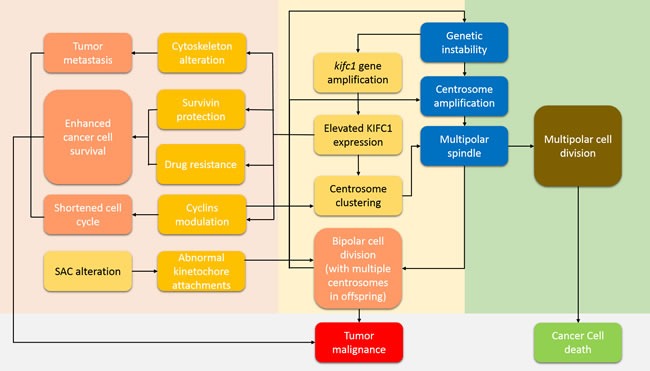
This pathway can be roughly divided into four areas. The grey area shows the final cancer cell condition. The light orange area shows a positive feedback cycle which we name the KIFC1-driven tumor malignancy cycle. Genetic instability induces centrosome amplification, which is a feature of cancer cells and enhances tumor malignancy, as well as kifc1 gene amplification [23]. Centrosome amplification induces the formation of multipolar spindles. Any failure in the turning of multipolar spindles into bipolar ones will eventually lead to cell death (the light green area) [42]. However, increased KIFC1 expression rescues cancer cells from such a death by assisting cells with multipolar spindle stability and by helping to achieve proper bipolar segregation through centrosome clustering activity [16, 40]. A proper bipolar cell division further stabilizes any genetic instability. Hence a positive feedback cycle is completed. The pink area illustrates other pathways of how KIFC1 drive tumor metastasis, enhance cell survival, and shorten the cell cycle so as to speed up cell proliferation.
