Table 4. The pharmacological details of the drugs currently in use or being developed for MCL. Please see Supplementary Table 4 to access complete table.
| FRONTLINE DRUGS | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Generic name Trade/Pipeline Name(s) | Company/FDA Approval year | Chemical structure | Drug Class | Status/Route | Target/Mechanism of action | Toxicity | References | |
| 1 |
Chlorambucil Leukeran Ambochlorin Amboclorin Linfozilin |
ASPEN GLOBAL INC, 1957 | 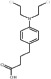 |
Alkylating agent | Prescription/Oral |
Target: DNA synthesis. Mechanism of action:
|
Hematologic: Bone marrow suppression, anemia, leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia. Gastrointestinal: Gastrointestinal disturbances Dermatologic: urticaria, angioneurotic edema, skin hypersensitivity. Other: pulmonary fibrosis, hepatotoxicity, fever, peripheral neuropathy, interstitial pneumonia, sterile cystitis, infertility, leukemia, secondary malignancies. |
[277] |
| 2 |
Lenalidomide Revlimid |
CELGENE, 2005 | 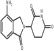 |
Immunomodulatory Agent | Prescription/Oral |
Target: TNF-alpha inhibitor. Mechanism of action:
|
Hematologic: Neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia. Other: pneumonia, fatigue. |
[278] |
| 3 |
Ibrutinib Imbruvica |
PHARMACYCLICS INC, 2014 | Antineoplastic Agent/Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor | Prescription/Oral |
Target: Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor Mechanism of action:
|
Gastrointestinal: Diarrhea, nausea, peripheral edema, constipation, vomiting, loss of appetite. Other: fatigue, dyspnea, upper respiratory tract infection. |
[279] | |
| 4 |
Methotrexate TrexallRasuvoOtrexupMexate |
BARR, 2001MEDAC PHARMA INC, 2014ANTARES PHARMA INC, 2013BRISTOL, 1979 | Antineoplastic Agent, Antipsoriatic, Antirheumatic, Cytotoxic | Prescription/Injection, Sub-cuteneous |
Target: Dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor Mechanism of action:
|
Hematologic: aplastic anemia, pancytopenia, leukopenia, neutropenia. Other: lymphadenopathy, drowsiness, blurred vision, cognitive dysfunction, moodiness, tinnitus, mucositis. |
[280] | |
| 5 |
Fludarabine FludaraOforta |
GENZYME CORP, 1991SANOFI AVENTIS US, 2008 | Purine Nucleotides, Antimetabolites Antineoplastic Agents | Prescription/Intravenous, Oral |
Target: DNA synthesis inhibitor Mechanism of action:
|
Hematologic: neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, lymphocytopenia. Gastrointestinal: nausea, vomiting. Other: infection (typically respiratory tract), fever, elevation of liver enzymes. |
[281] | |
| 6 |
Ibritumomab tiuxetan Zevalin |
SPECTRUM PHARMS, 2002 | Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives | Prescription/Intravenous |
Target: CD20 Mechanism of action:
|
Hematologic: Haemopoetic, myelosuppression | [282] | |
| 7 |
Temsirolimus Torisel |
PF PRISM CV, 2007 | 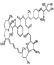 |
mTOR inhibitor, Antineoplastic agent | Prescription/Intravenous |
Target: mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor Mechanism of action:
|
Hematologic: thrombocytopenia, asthenia, anemia. Gastrointestinal: diarrhea. Other: fever. |
[283] |
| 8 |
Cyclo-phosphamide CytoxanNeosar |
BAXTER HLTHCARE, 1959TEVA PARENTERAL, 1993BEDFORD, 1982 | Alkylating agents | Prescription/Oral, intravenous |
Target: DNA Mechanism of action: Forms DNA crosslinks both between and within DNA strands at guanine N-7 positions leading to cell apoptosis. |
Dermatologic: alopecia. Other: haemorrhagic cystitis, immunosuppression (when not desired). |
[284] | |
| 9 |
Vincristine Marqibo Kit Oncovin Vincrex Vincasar PFS Leurocristine |
TALON THERAP, 2012LILLY, 1963BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB, 1988TEVA PARENTERAL, 1987 | 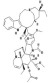 |
Antineoplastic Agents, Phytogenic | Prescription/Intravenous |
Target: beta-tubulin, tubulin polymerization inhibitor Mechanism of action:
|
Other: acute uric acid nephropathy, acute shortness of breath and severe bronchospasm. | [285] |
| 10 |
Doxorubicin Adriamycin PFS Rubex Doxil |
PHARMACIA AND UPJOHN, 1987BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB, 1989JANSSEN RES AND DEV, 1995 | 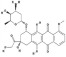 |
Antibiotics, Antineoplastic, Anthracyclines. | Prescription/Intravevous |
Target: topoisomerase II inhibitor Mechanism of action:
|
Other: acute and chronic cardiotoxicity/cardiomyopathy. | [286] |
| 11 |
Dexamethasone Ciprodex Decaderm Decadron Dexamethasone Hexadrol Maxidex Ozurdex Tobradex ST |
ALCON PHARMS LTD, 2003 MERCK, N/AMERCK, 1958 ECR, 2008 SANDOZ, 1971 WATSON LABS, 1973 PVT FORM, 1973 PHOENIX LABS NY, 1974 MUTUAL PHARM, 1974 ROXANE, 1975 STI PHARMA LLC, 1976 PAR PHARM, 1983 LYNE, 2011 VINTAGE PHARMS, 2011 ORGANON USA INC, 1962 ALCON, 1962 ALLERGAN, 2009 ALCON PHARMS LTD, 2009 | 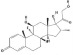 |
Glucocorticoid, Corticosteroid | Prescription/intravenous, intramuscular, intra-articular, intralesional and soft tissue injection |
Target: glucocorticoid receptor agonist Mechanism of action: Inhibition of inflammatory agents in the body, implicated in the development or growth of some cancers. |
Gastrointestinal: gastritis. Other: cushingoid facies, obesity, glucose intolerance, hypertension, psychologic alterations, infections, myositis and myopathy, avascular necrosis of bone. |
[287] |
| 12 |
Cytarabine Cytosar-UDepocyt |
TEVA PARENTERAL, 1969 EUROHLTH INTL SARL, 1989 HOSPIRA, 1990 FRESENIUS KABI USA, 2004 MYLAN LABS LTD, 2011 TEVA PHARMS USA, 1998 PACIRA PHARMS INC, 1999 | Antimetabolite antineoplastic agent, Nucleoside Metabolic Inhibitor | Prescription/Intravenous, Intrathecal, or Subcutaneous |
Target: DNA polymerase inhibitor Mechanism of action:
|
Hematologic: anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, megaloblastosis. Other: infection, Ara-C syndrome. |
[288] | |
| RELAPSED DRUGS | ||||||||
| 13 |
Bendamustine Treanda Ribomustin Levact Cytostasan SDX-105 |
CEPHALON, 2008 | Alkylating/Antineoplastic Agent | Prescription/intravenous injection |
Target: DNA Mechanism of action: Activation of DNA damage stress response and apoptosis induced by p21 (Cip1/Waf1) and Noxa, inhibition of mitotic checkpoints, and induction of mitotic catastrophe |
Hematologic: febrile neutropenia. Other: fatigue, pneumonia, hypokalemia dehydration, pyrexia. |
[289] | |
