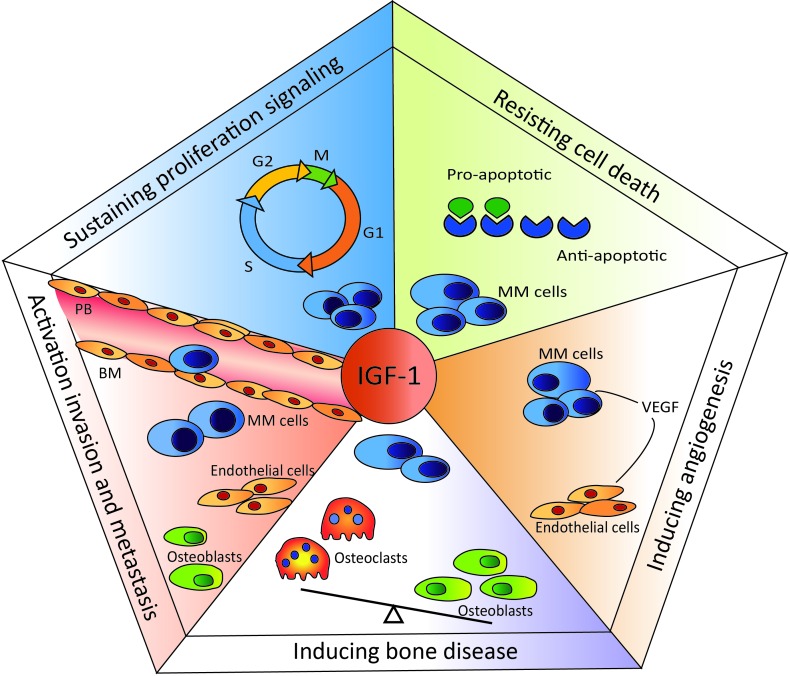
Figure 2. Role of IGF-I in multiple myeloma-specific hallmarks.
IGF-I is involved in the homing process, attracting the MM cells from the peripheral blood (PB) into the BM microenvironment. Once in the BM, IGF-I stimulates the proliferation of MM cells. Moreover, IGF-I up- and down-regulates the expression of anti- and pro-apoptotic molecules, respectively, protecting MM cells from (drug-induced) apoptosis. Another important hallmark of MM is the induction of angiogenesis. IGF-I stimulates VEGF secretion by the MM cells, enhancing angiogenesis. IGF-I is also involved in myeloma-associated bone disease by promoting osteoclast maturation and activity.