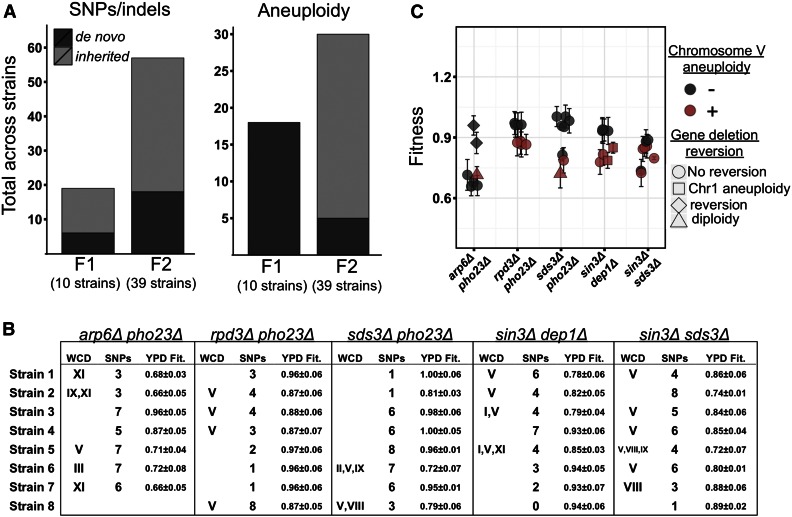
Figure 3.
Segregating and de novo genetic variation revealed by whole-genome sequencing. (A) Total number of unique SNPs, or small indels (left), or aneuploidy events (right), observed across all F1 or F2 strains for which both parental strains had been sequenced (N = 10 and N = 39 strains, respectively). Bars are shaded by whether the observed variant was observed in a parental strain (light gray), or appeared to have occurred de novo during strain generation (dark gray). (B) For each of the strains sequenced (rows) in each of the double deletion groups, “WCD” indicates identities of duplicated chromosomes, “SNPs” indicates the total number of single nucleotide polymorphisms or small indels observed, and “YPD Fit.” indicates iSeq estimate in YPD. (C) Fitnesses for each whole-genome sequenced F2 strain. Color indicates chromosome V duplication events, and shape indicates gene reversion events in which sequencing reads mapped to one or two genic region(s) expected to be deleted. Error bars are the SD of estimates across three biological replicates.