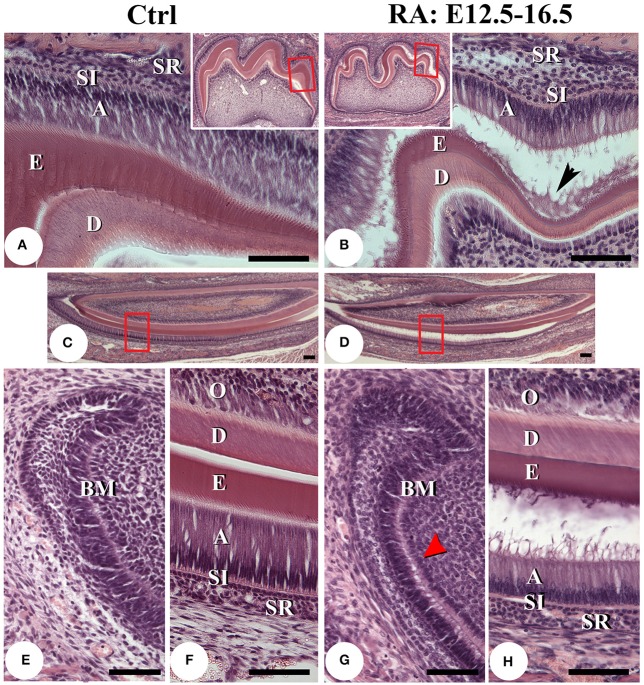
Figure 3.
Histological analysis of post-natal day 7 teeth. Hematoxylin and eosin stained sagittal sections of lower first molars of control (A) and E12.5–16.5 RA-treated (B) mice. The boxed areas in low-magnification insert panels are shown in detail. A black arrowhead in B points to cell debris accumulating between separated tissue layers. Lower incisors of untreated (C,E,F) and RA-treated (D,G,H) mice. F, H are higher magnification views of the boxed areas in C,D. Comparing the cervical loop of untreated (E) with RA-treated mice (G), it appears retinoid excess may disrupt the basement membrane (G, red arrowhead), potentially leading to ameloblast detachment (B,D,H). The secretory stage ameloblast layer is also slightly thinner and enamel thickness reduced after RA treatment (B,D,H). Scale bars: 100 μm. Abbreviations: A, ameloblasts; BM, basement membrane; D, dentin; E, enamel; O, odontoblasts; SI, stratum intermedium; SR, stellate reticulum.