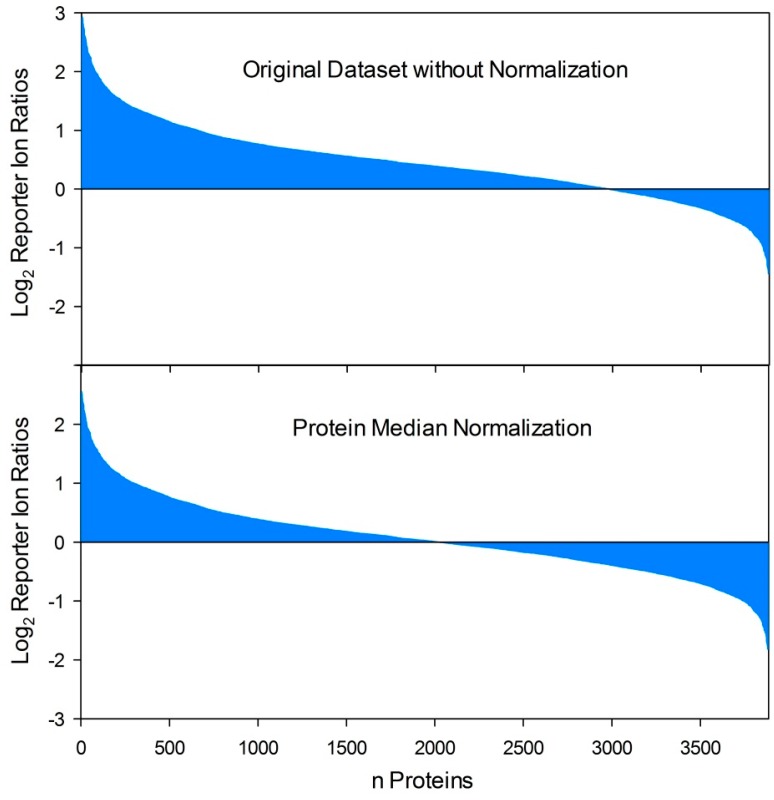
Figure 2.
Effects of protein normalization procedures on quantitative proteome datasets. By comparison of two proteome conditions (e.g., host-pathogen interaction versus control) based on reporter ion quantification procedures (iTRAQ, TMT) the respective ratio calculation resulted in an uneven distribution of protein fold changes if varying total protein concentrations were compared. In this example, this results in several false positive “upregulated” reporter ion ratios while the ratios of moderate down-regulated proteins (depending on the applied threshold value for differential regulation) are dropped under the threshold value as false negatives. In contrast, protein median normalization resulted in an even distribution of protein fold changes and is capable to equalize disproportionate samples and allow comparability in a relatively quantitative manner.