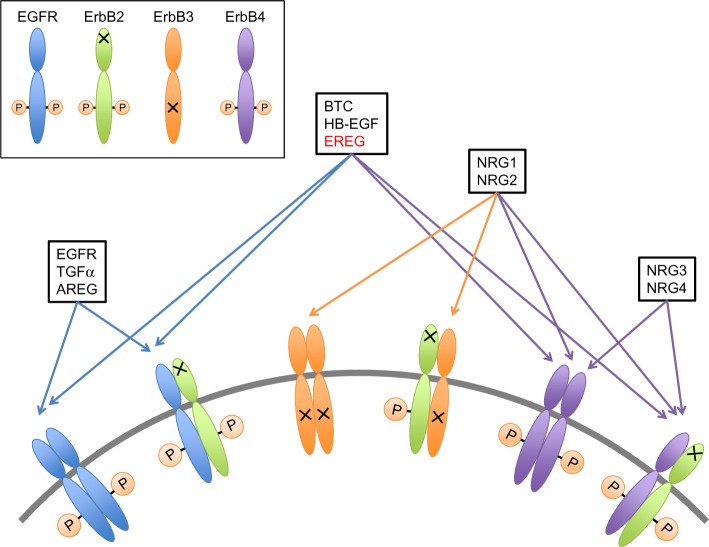
Figure 1.
Binding specificity of EGF, transforming growth factor-α (TGF-α), amphiregulin (AREG), betacellulin (BTC), heparin-binding EGF (HB-EGF), EREG, and neuregulins (NRGs).
Notes: EGFR, TGF-α, and AREG bind specifically to EGFR. BTC, HB-EGF, and EREG bind both EGFR and ErbB4. NRGs are further categorized according to their capacity to bind ErbB3 and ErbB4 (NRG1 and NRG2) or only ErbB4 (NRG3 and NRG4). ErbB2 has no binding EGF family ligands, whereas it serves as a heterodimerization partner of the other ligands. ErbB3 lacks intrinsic kinase activity, but it can activate EGFR signaling pathways through heterodimerizing with another ErbB receptor.
Abbreviation: EREG, epiregulin.