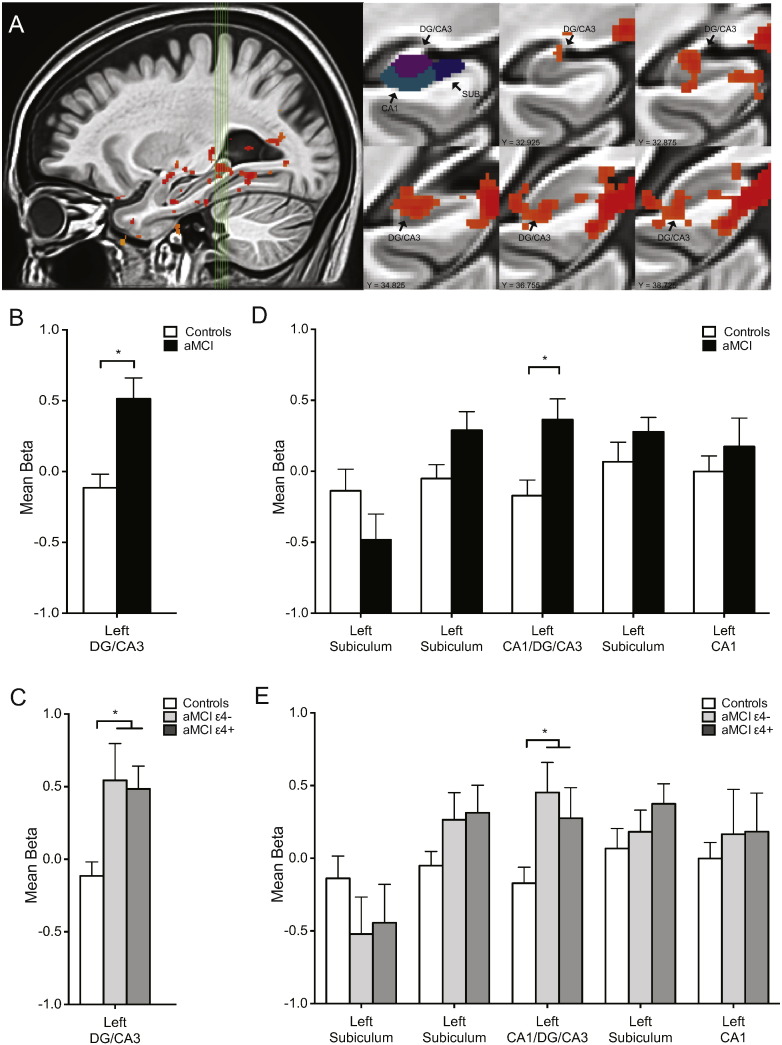
Fig. 3.
Increased hippocampal DG/CA3 activation in the context of impairment memory performance is observed equally in aMCI ApoE-4 carriers and aMCI ApoE-4 non-carriers. A. Sagittal view of the left medial temporal lobe. Green vertical lines identify slices through the hippocampus shown on the right. First coronal slice shows the segmentation of different hippocampal regions of interest including dentate gyrus/CA3 (DG/CA3), CA1 and subiculum (SUB). Coronal slices show statistical maps of the extent of task related activity in the left DG/CA3 from anterior to posterior. B. Patients with aMCI show increased activity in the left DG/CA3 compared to healthy control subjects during critical lure trials. C. Increased activation is observed equally in aMCI ApoE-4 carriers and aMCI non-carriers in the left DG/CA3. D. Patients with aMCI showed increased activation in the left CA1/DG/CA3. No other differences were observed between aMCI patients and healthy control subjects in other clusters of task related activation in the hippocampus. E. Increased activation is observed equally in aMCI ApoE-4 carriers and aMCI non-carriers in the left CA1/DG/CA3. No other differences were observed between aMCI ApoE-4 carriers and aMCI ApoE-4 non-carriers in other clusters of task related activation in the hippocampus. Comparisons are based on independent sample t-tests. Values are means ± SEM. *p < 0.05.