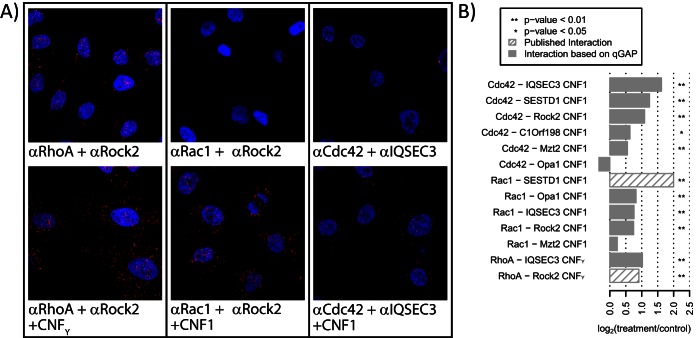
Fig. 5.
Validation of loading-state-dependent interactions in situ with the proximity ligation assay (PLA). (A) Cells were treated with CNFY (for RhoA activation) or with CNF1 (Cdc42 and Rac1 activation), fixed, costained with oligonucleotide-coupled antibodies against the Rho GTPase and interactors. The basal PLA signal (red) increased upon toxin treatment for RhoA-Rock2 (known interaction), Rac1-Rock2 and Cdc42-IQSEC3 (both novel). (B) Automated quantification shows that toxin treatment significantly increased PLA signals for 9/11 tested novel interactions.