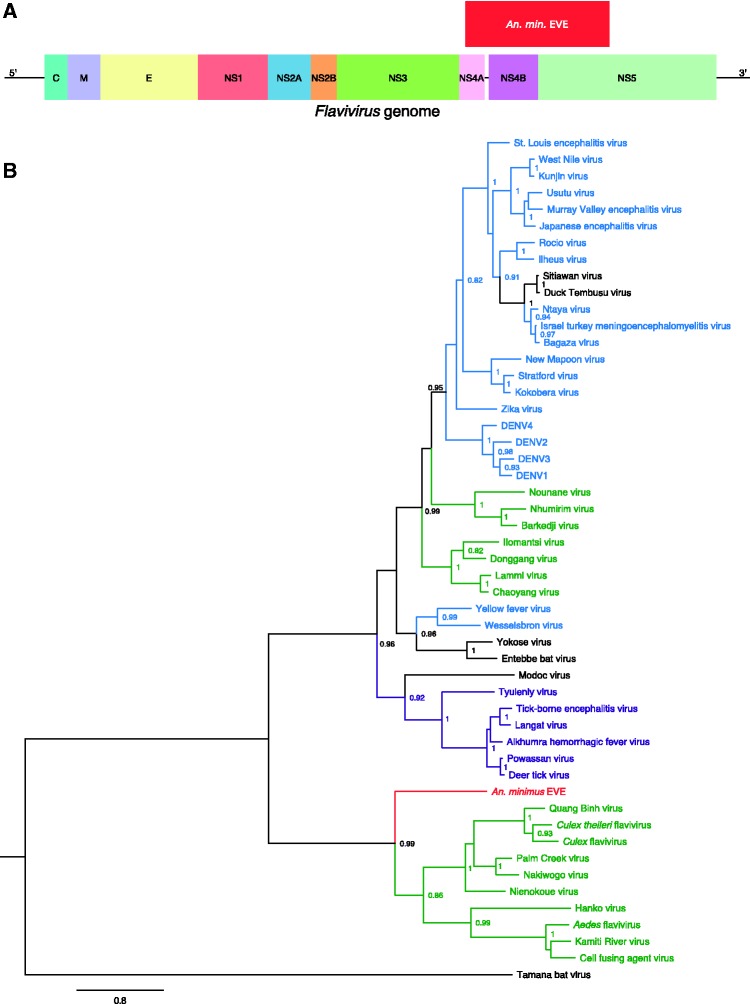
Figure 1.
Discovery of a flavivirus-derived EVE in An. minimus. (A) EVE location in a generic Flavivirus genome. Positioning is based on the genome sequence of Nienokoue virus (GenBank accession no. JQ957875). C, capsid protein; E, envelope glycoprotein; M, membrane glycoprotein; NS1, non-structural glycoprotein 1; NS2A, non-structural protein 2A; NS2B, non-structural protein 2B; NS3, non-structural protein 3 (protease/helicase); NS4A, non-structural protein 4A; NS4B, non-structural protein 4B; NS5, non-structural protein 5 (RNA-dependent RNA polymerase). (B) Phylogenetic relationships of the newly discovered An. minimus flavivirus-derived EVE with exogenous flaviviruses. Maximum likelihood trees were constructed based on the translated EVE sequence. Clades are color-coded according to known host specificity: green, ISFs; purple, tick-borne arboviruses; black, ‘NKV’ (vertebrate specific); blue, mosquito-borne arboviruses; red: EVEs. Scale bar indicates the number of substitutions. Node values represent Shimodaira-Hasegawa (SH)-like branch support (only values > 0.8 are shown).