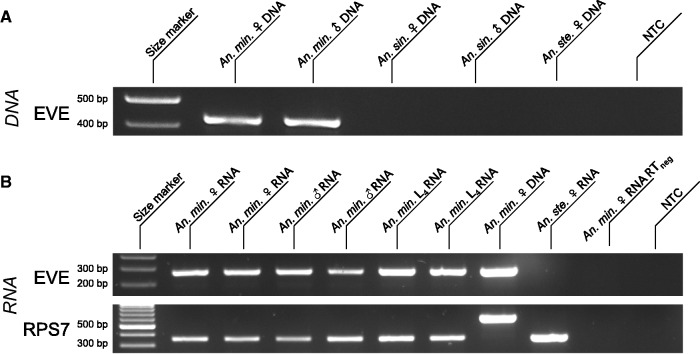
Figure 2.
In vivo detection of the An. minimus flavivirus-derived EVE. (A) EVE detection in genomic DNA. Lane 1: size marker; lane 2: amplified genomic DNA from a pool of 10 An. minimus adult females; lane 3: amplified genomic DNA from a pool of 10 An. minimus adult males; lane 4: amplified genomic DNA from a pool of 10 An. sinensis adult females; lane 5: amplified genomic DNA from a pool of 10 An. sinensis adult males; lane 6: amplified DNA from a pool of 10 An. stephensi females; lane 7: no template control (NTC). (B) EVE detection in total RNA. Lane 1: size marker; lanes 2 and 3: amplified cDNA from pools of five adult females; lanes 4 and 5: amplified cDNA from pools of five adult males; lanes 6 and 7: amplified cDNA from pools of five L4 larvae; lane 8: amplified DNA from a pool of 10 females; lane 9: amplified cDNA from a pool of 5 An. stephensi females; lane 10: DNA contamination control (no reverse transcription) using the same pool of five adult females as lane 2; lane 11: NTC. First row: EVE; second row: RPS7 (control gene). The RPS7 target DNA sequence includes an intron, so that DNA contamination is expected to result in a larger PCR product.