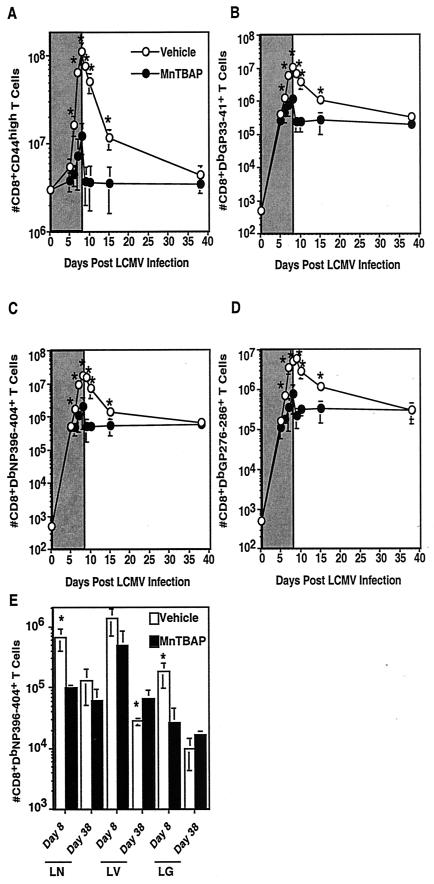
FIG.3.
Treatment with MnTBAP results in decreased expansion and contraction of CD8+ T cells during primary viral infection. C57BL/6 mice were treated with either the vehicle or 5 mg of MnTBAP/kg and then infected with LCMV Armstrong. A maintenance dose was administered every 24 h. At the indicated time points, mice were sacrificed, the spleen was removed, and cells were stained with anti-CD8α and either anti-CD44 (A), DbGP33-41 (B), DbNP396-404(C), or DbGP276-286 (D). The numbers of activated (A) and antigen-specific CD8+ T cells (B-D) were quantitated, and the averages and standard deviations are shown. To determine the effect of MnTBAP administration on lymphocyte numbers in other tissues, mice were sacrificed on days 8 and 38 postinfection and lymphocytes were isolated from the lung, liver and lymph nodes and stained with anti-CD8α and DbNP396-404 (E). The numbers of NP396-404-specific CD8+ T cells were quantitated, and the average and standard deviation are shown. Six to 10 mice were analyzed at each time point. The gray areas in panels A through D indicate the windows of treatment. *, significant difference between vehicle- and MnTBAP-treated mice; P ≤ 0.05.