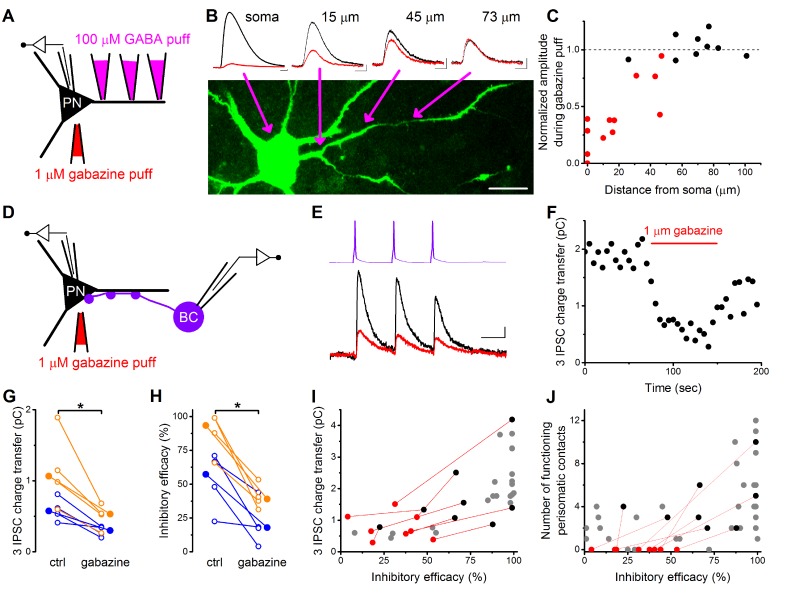
Figure 6. Pharmacological elimination of perisomatic contacts significantly reduces the inhibitory efficacy.
(A) Schematic drawing of the experiment determining the area affected by local somatic gabazine application. (B) Representative recordings of the GABA puff evoked currents at various dendritic locations in control conditions (black) and upon somatic gabazine application (red). (C) Summary of recordings from 22 dendritic locations show that the somatic gabazine puff can significantly reduce GABAergic currents (red dots) in an area of 50 µm radius from the site of the application, which covers the perisomatic region. (D) Schematic drawing of the experiment measuring the effect of the elimination of perisomatic contacts by local somatic gabazine application. (E and F) Representative experiment showing the rapid and substantial drop in IPSC charge transfer upon gabazine application (applied for 75 s in panel F). (G and H) Elimination of perisomatic inhibitory inputs resulted in a significant suppression of the IPSC charge transfer and inhibitory efficacy (p=0.01 and p=0.007, respectively, Wilcoxon Signed Rank test). Blue: CCKBC-PN pairs, orange: PVBC-PN pairs. Open circles represent recorded pairs, filled circles represent median values. (I and J) Relationship between the inhibitory efficacy and IPSC charge transfer (I) or the number of functioning perisomatic contacts (J) before (black dots) and after (red dots) the pharmacological elimination of perisomatic inhibition (individual experiments connected with red line). Grey dots show data from previous recordings for comparison (data from Figures 2F and 5F). Scales: B: 20 pA and 50 ms; 20 µm, E: 8 pA and 20 ms.