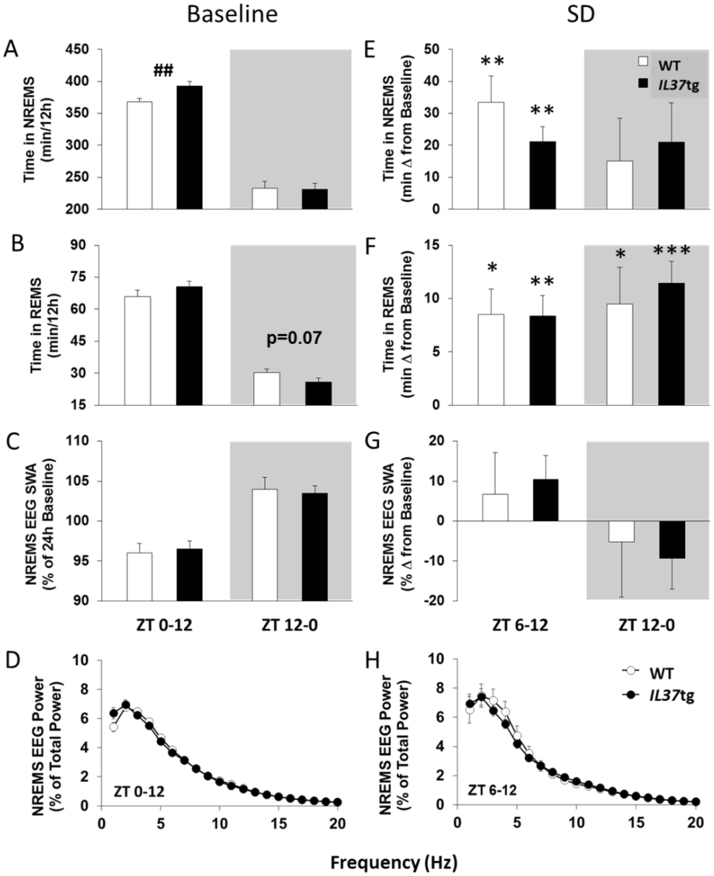
Fig. 1.
IL37tg mice have more spontaneous NREMS and similar sleep rebounds compared to WT mice. NREMS amounts [A], REMS amounts [B] and NREMS EEG SWA [C] in 12 h periods corresponding to the light or dark phase (gray fill) for WT mice (white bars; n=24) and IL37tg mice (black bars; n=23; ## p<0.01, WT vs. IL37tg) are shown. NREMS EEG power [D] during the 12 h light period (ZT0-12) is depicted. After 6 h sleep deprivation, NREMS amounts [E], REMS amounts [F] and NREMS EEG SWA [G] in the subsequent 6 h light period and 12 h dark period (shaded areas) for WT (n=7) and IL37tg mice (n=9) are expressed as change from baseline values. NREMS EEG power [H] during the 6 h light period following sleep deprivation (ZT6-12) is reported (all data expressed as mean±SEM; asterisks indicate within strain, treatment differences,* = p<0.05; ** = p<0.01; *** = p<0.001).