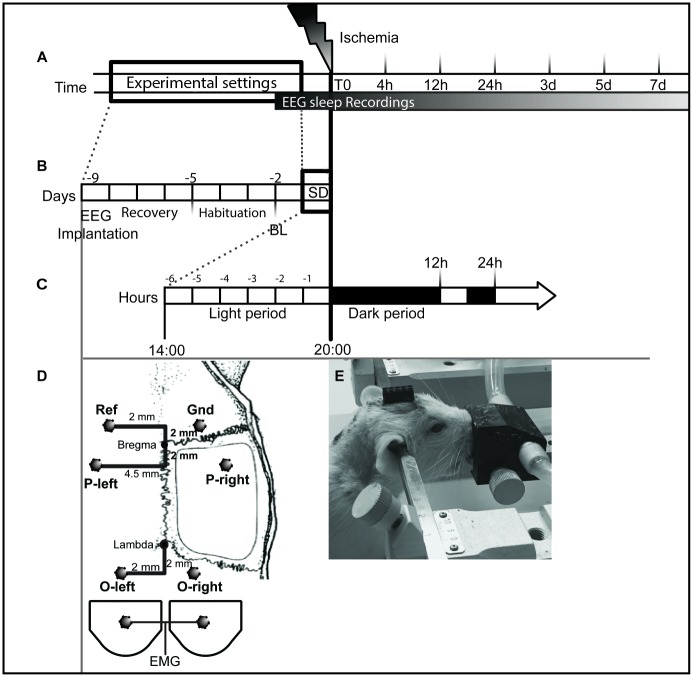
Fig 1. Schematic of the experiment design.
(A) Design for the sleep architecture analysis and for the time course of gene expression of MCH and OX systems. Ischemia surgery was performed on day 0, and then the rats were sacrificed at 4, 12 and 24 hours (acute phase) and 3, 4 and 7 days (chronic phase) following ischemic surgery. Baseline was recorded 2 days before ischemia for 24h; 12h dark and 12h light. Rats subjected to SD were also recorded over 6h of SD. The EEG/EMG recordings were stopped when animals were sacrificed; represented by each time point (B) Design for sleep architecture. Rats were implanted with EEG/EMG electrodes and then allowed to recover for 4 days, and then connected to a flexible cable and swivel and habituated for 3 days with a cable, before EEG/EMG recording. C) Design for SD interventions. SD was performed by gentle handling during the last 6 h of the light period; from 14:00 to 20:00. And ischemia/sham surgery was performed immediately after; at the beginning of the dark period, during either stroke or sham surgery EEG/EMG recordings were not performed (D) Not-to-scale representation of the placement of the screw electrodes over the parietal cortex and the cerebellar cortex (dark circles), Ref. = reference and Gnd = ground. EMG was bilaterally placed in the neck muscle using wire electrodes (E) An anesthetized rat fixed to the stereotaxic frame with EEG/EMG plug fixed to the skull with dental cement. Experimental groups: i. SD_IS (n = 6); ii. IS (n = 6); iii. SD_Sham (n = 4); and iv Sham (n = 6). Electroencephalogram (EEG); Electromyogram (EMG).