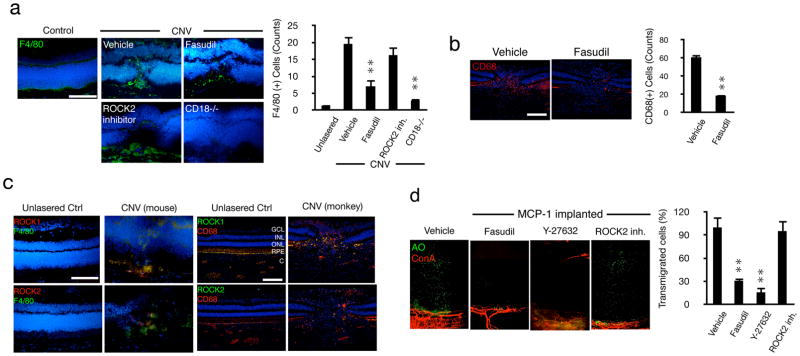
Figure 4. ROCK-mediated regulation of inflammatory leukocyte infiltration during CNV.
(a) Representative micrographs of laser-induced CNV lesions, immunostained for F4/80 in C57BL/6J mice treated with vehicle, fasudil or ROCK2 inhibitor, or in CD18−/− mice and quantification of the number of F4/80-positive macrophages in CNV lesions (n=3 animals in each group). In each eye 6 lesions were placed. From each lesion 10 or more sections were stained, the results of which were averaged for each lesion/animal. Scale bar, 100μm. (b) Impact of fasudil on macrophage infiltration in laser-induced CNV in monkey (n=4). Representative micrographs of CNV lesions, immunostained for CD68 in lasered monkeys treated with vehicle or fasudil. Quantification of the number of CD68-positive leukocytes in CNV lesions (n=4). **P< 0.01. Scale bar, 100μm. (c) Double immunostaining of laser-induced CNV in monkey and mice with Abs of ROCK1 or ROCK2 and CD68 or F4/80. GCL, ganglion cell layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; RPE, retinal pigmented epithelial layer; C, choroid. Bar, 50μm. (d) Ex vivo imaging of impact of ROCK inhibitors on MCP-1-mediated leukocyte transmigration. AO(+) leukocytes and Con A(+) angiogenic vessels in MCP-1-implanted corneas, 2h after AO injection, 24 hours after pellet implantation with vehicle, fasudil, Y-27632 or ROCK2 inhibitor treatment. Quantification of the number of AO(+) leukocytes in areas of MCP-1-implanted corneas 2h after AO injection, 24 hours after pellet implantation. n=4; *P< 0.05, **P< 0.01.