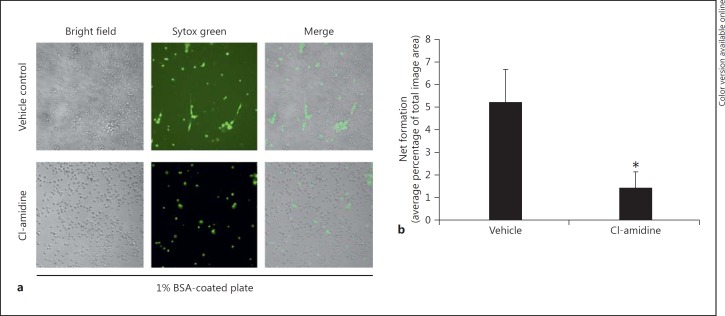
Fig. 3.
Cl-amidine treatment in vivo reduces NET formation in murine neutrophils ex vivo. Septic mouse lavage contents were placed on tissue culture plates coated with 1% BSA (with no additional stimulation) incubated at 37°C for 1–2 h, and stained with Sytox green for extracellular nucleic acid visualization. a Peritoneal cells from Cl-amidine-treated mice display a decrease in extracellular nuclear material (NET formation) compared to control cells at 1–2 h. Original magnification ×20. b This reduction in NET formation is statistically significant when quantified as the percent area of the totaled imaged field. (Data represent 4–6 wells per condition.) * p < 0.05, ANOVA analysis with Newman-Keuls post hoc analysis or unpaired-sample two-tailed Student's t test as appropriate.