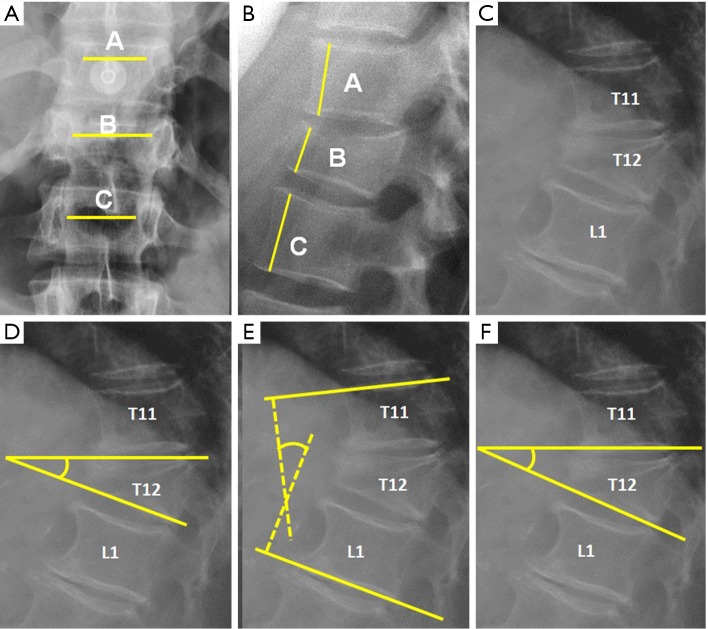
Figure 2.
Radiological measurements in plain film radiography. (A) Interpedicular distance measured from the closest point of the medial aspect of both pedicles. Percentage of widening of the interpedicular distance can be calculated by the following formula, where A is the interpedicular distance of the normal superior vertebra, B is the interpedicular distance at the fractured vertebra and C is the interpedicular distance of the normal inferior vertebra: ; (B) Anterior vertebral height. The percentage of vertebral height loss can be calculated by the following formula, where A is the height of normal superior vertebra, B is the height of the fractured vertebral body and C is the height of normal inferior vertebra: ; (C) Wedge fracture of T12; (D) local Kyphosis is the angle between both endplates of fractured vertebra; (E) regional kyphosis is the angle between the upper endplate of the vertebra overlying the fractured vertebral body and the lower endplate of the vertebra underlying the fractured vertebral body; (F) segmental kyphosis (SK) is the angle between the inferior endplate of the injured vertebra and the inferior endplate of the overlying vertebra (segment = injured vertebra + overlying disc).