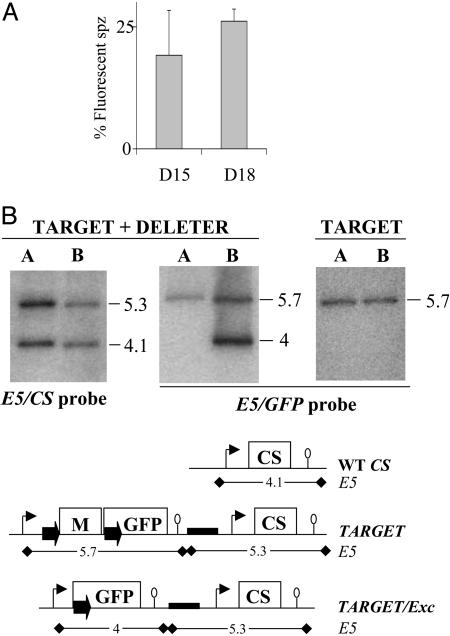
Fig. 3.
Progeny of a TARGET × DELETER cross. (A) The TARGET and DELETER clones were mixed in equal proportions in the same mouse and transmitted to 100 A. stephensi female mosquitoes. The percentage of fluorescent sporozoites (spz) observed in the salivary glands of infected mosquitoes at days 15 and 18 postinfection is ≈25% on average (mean of three experiments). Bars represent standard deviation values. (B) Southern hybridization of genomic DNA of the TARGET + DELETER mixture or the TARGET clone alone collected from mouse A (before mosquito infection) and mouse B (after mosquito infection). The predicted size (in kilobases) of restriction fragments generated by digestion with EcoRV (E5) at the CS, TARGET, and TARGET/Exc loci are shown. The CS probe shows a similar intensity of the EcoRV fragments corresponding to the WT CS (4.1 kb) and the TARGET + TARGET/Exc loci (5.3 kb) in both mouse A and mouse B. The GFP probe shows a similar intensity of the EcoRV fragments corresponding to the TARGET (5.7 kb) and the TARGET/Exc (4 kb) loci in mouse B. Therefore, ≈25% of all RBC stages from mouse B after the cross have a TARGET/Exc locus. The 4-kb band is not detected in mouse B when the TARGET clone is cycled alone.