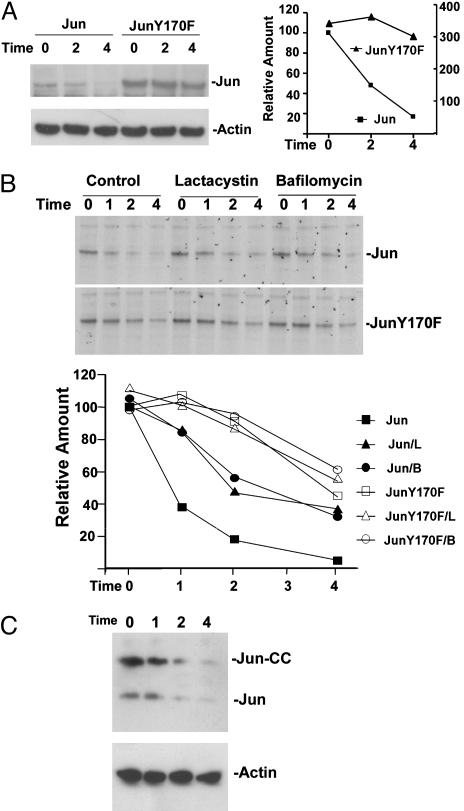
Fig. 6.
Stabilization of Jun by the Y170F mutation and by inhibitors of proteasomes and lysosomal H+-ATPase. (A) Jun and JunY170F with Xpress epitope tags were expressed in HEK293T cells. Fifty micromolar cycloheximide was added 24 h after transfection (Time 0). The cells were harvested at the times (h) indicated above the lanes, and cell extracts were analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies directed against the Xpress tag (Left Upper) and actin (Left Lower). The relative amounts of Jun were quantified and are plotted in the graph (Right) (Jun levels are plotted on the left axis, and JunY170F levels are plotted on the right axis). (B) COS-1 cells that expressed Jun (Top) or JunY170F (Middle) with Xpress epitope tags were labeled with 35S amino acids. The radiolabel was washed out (Time 0), and the cells were cultured in the absence (Control) or in the presence of 20 μM lactacystin or 0.5 μM bafilomycin A. The cells were harvested at the times indicated above the lanes, and proteins were precipitated by using anti-Xpress antibodies and resolved by SDS/PAGE. The amounts of Jun (filled symbols) and JunY170F (open symbols) were quantified and plotted in Bottom (L, lactacystin; B, bafilomycin). (C) Jun-CC was expressed in COS-1 cells. Cycloheximide was added 24 h after transfection (Time 0). The cells were harvested at the times indicated above the lanes (h), and cell extracts were analyzed by Western blotting by using antibodies directed against Jun (Upper) and actin (Lower). The bands corresponding to transiently expressed Jun-CC and endogenous Jun are indicated.