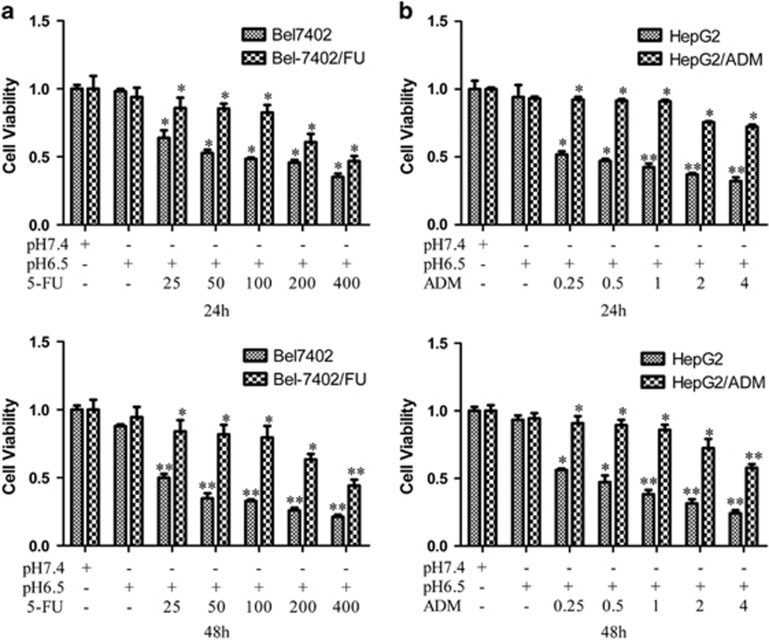
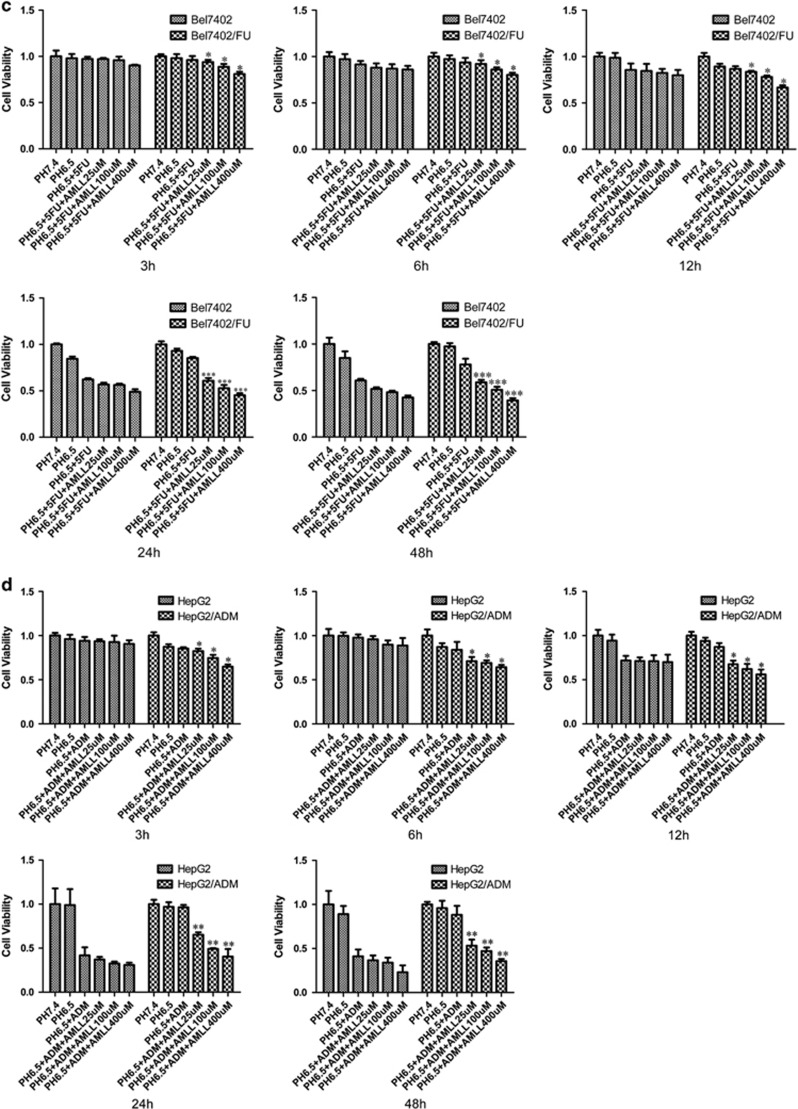
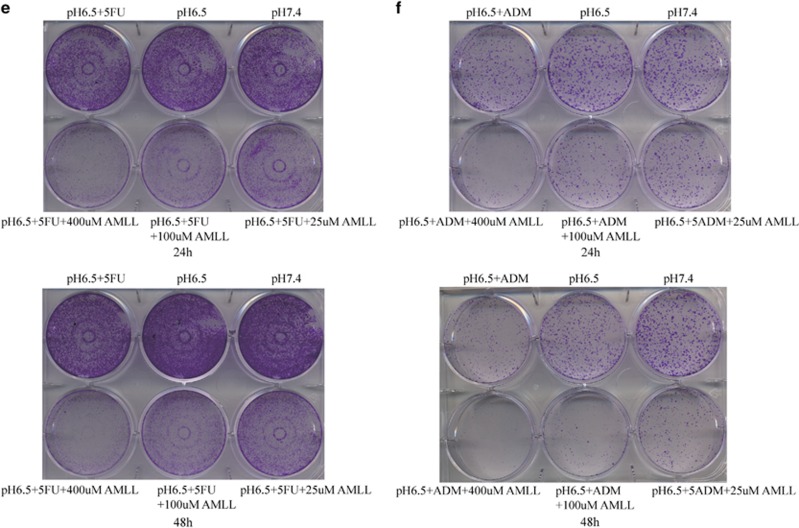
Figure 3.
Inhibition of the activity of ASIC1a enhances the chemosensitivity of Bel7402/FU and HepG2/ADM cells. (a and b): Chemosensitivity of Bel7402/FU and HepG2/ADM cells by MTT assay. MTT assays were conducted at 24 and 48 h. The concentrations of 5-FU were 25, 50, 100, 200, and 400 mg/l, and the concentrations of ADM were 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 mg/l. (c and d): Effect of the activity of ASIC1a effect on drug resistance by MTT assay. MTT assays were conducted at 3, 6, 12, 24, and 48 h. The concentration of 5-FU was 100 mg/l, the concentration of ADM was 1 mg/l, the concentrations of amiloride were 25, 100, and 400 μmol/l. Data were expressed as the mean±s.d., *P<0.05 versus pH6.5+5FU or pH6.5+ADM group, **P<0.01 versus pH6.5+5FU or pH6.5+ADM group, ***P<0.001 versus pH6.5+5FU or pH6.5+ADM group. (e): Effect of the activity of ASIC1a effect on drug resistance by colony formation assay in Bel7402/FU cells. The concentration of 5-FU was 100 mg/l, and the concentrations of amiloride were 25, 100, and 400 μmol/l. (F): Effect of the activity of ASIC1a effect on drug resistance by colony formation assay in HepG2/ADM cells. The concentration of ADM was 1 mg/l, and the concentrations of amiloride were 25, 100, and 400 μmol/l. Colony formation assays were conducted at 24 and 48 h.