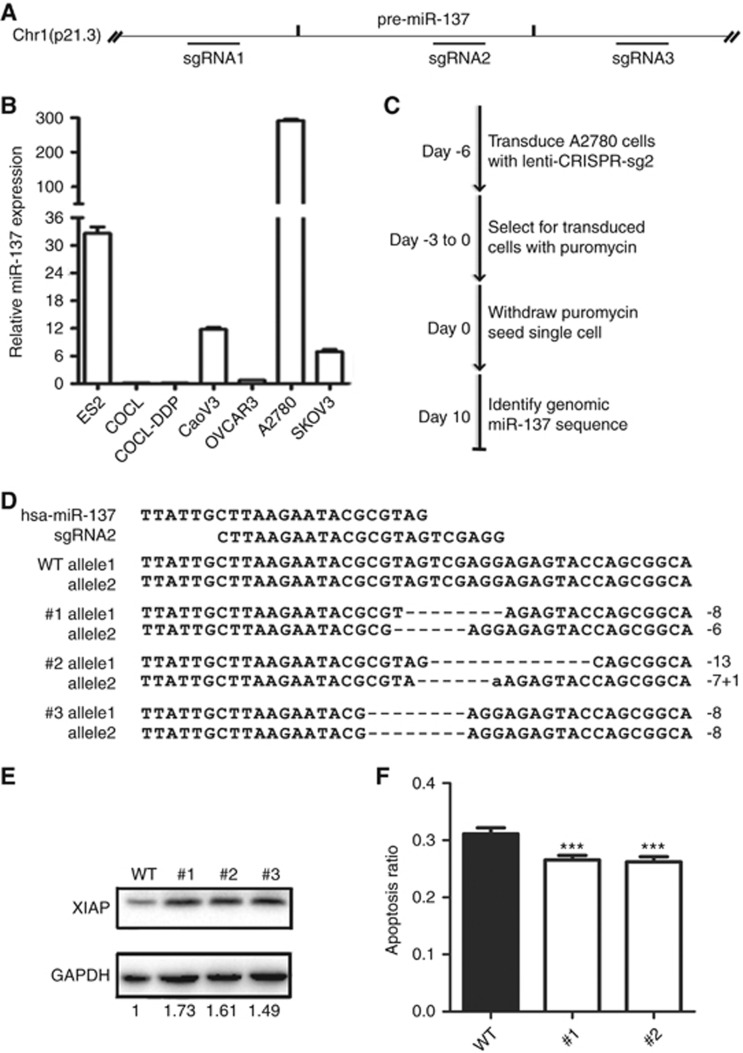
Figure 5.
miR-137 knockout via CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing up-regulates XIAP protein and inhibits apoptosis in A2780 cells. (A) The location of three designed sgRNAs that target genomic miR-137. (B) miR-137 expression in several ovarian cancer cell lines. (C) Timeline of miR-137 genome editing in the A2780 cell line. (D) Representative sequences of the mutated alleles from #1, #2, #3 single-cell clones derived from sgRNA2. Black dashes, deleted bases; lowercase bases, insertions. (E) XIAP protein levels of the four clones and wild-type A2780 cells (WT) in D. (F) The apoptosis ratios of the wild-type A2780 cells (A2780 WT) and #1 and #2 clones were determined as shown in Figure 4A. The same amount of wild-type A2780 cells (WT) and cells of the #1 and #2 clones were seeded in 48-well plates, followed by treatment with 10 μM cisplatin 24 h later. DAPI staining of the cells' apoptotic nuclei was performed after 48 h. The apoptotic rate was expressed as the ratio of the number of the cells with apoptotic nuclei to the total number of DAPI-positive cells. The average values±s.d. of three separate experiments were plotted, and significant differences from the control value are indicated by ***P<0.001.