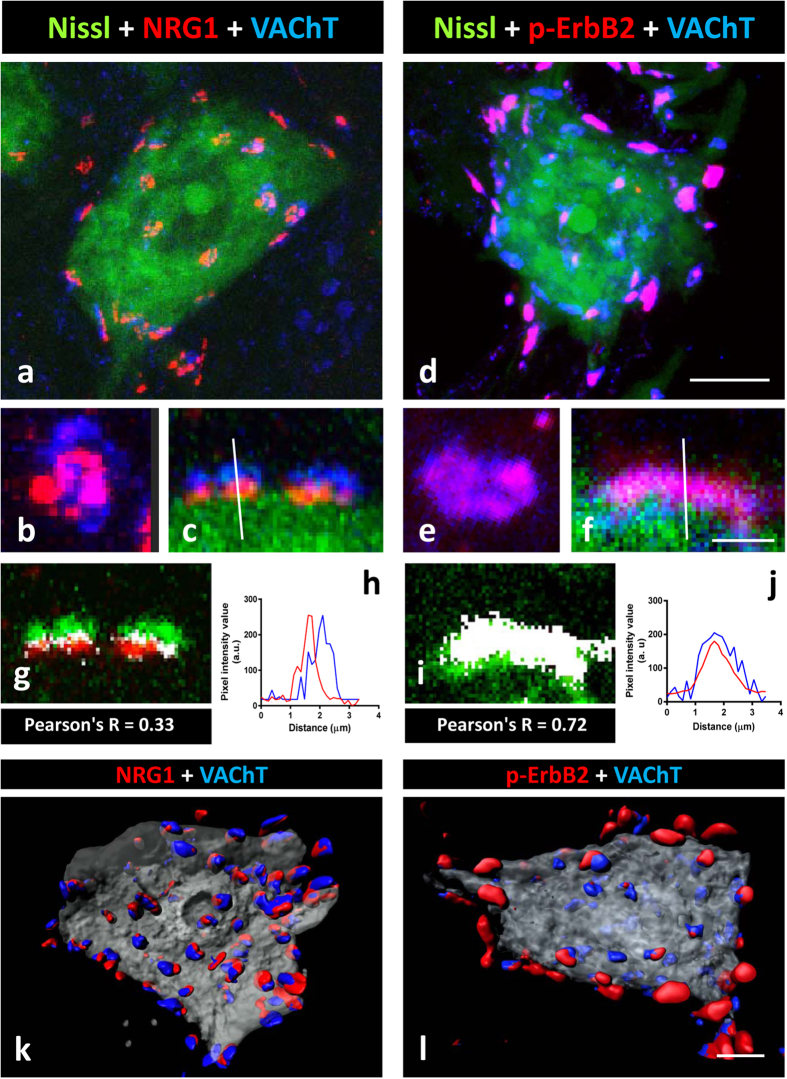
Figure 4. C-bouton type synapses contain the NRG1/ErbB signalling module.
(a,b,c) NRG1 (red) is concentrated at the C-bouton postsynaptic site adjacent to VAChT (blue) positive cholinergic terminals. (d,e,f) show that p-ErbB2 (red) is present in the presynaptic site of many, but not all, cholinergic terminals labelled with VAChT antibody (blue). In (a,c,d,f) MN somata are visualised with fluorescent Nissl staining (green). In (b) and (c), orthogonal and lateral projections, respectively, of a C-bouton immunolabelled for NRG1 and VAChT are shown; the dissociation of the two signals is evidenced after colocalisation (g) and pixel profile analysis (i). In (e) and (f) orthogonal and lateral projections, respectively, of a C-bouton immunolabelled for p-ErbB2 and VAChT are also shown; the overlapping of two signals is evidenced after a colocalisation (h) and pixel profile analysis (j). Colocalised pixels are displayed in white in (g) and (i); the low numbers of white pixels in (g) corresponds to the boundary between pre- and post-synaptic compartments, which are overlapped due to mechanical folding and compression inherent to tissue processing. (k,l) represents the volume rendering of serial optical sections (0.5-μm thick) from a MN showing the distribution of NRG1 (red in (k)) and p-ErbB2 (red in (l)), and VAChT (blue) co-labelled C-boutons. Scale bars: in (d) = 10 μm (also applicable to (a)); in (f) = 3 μm (also applicable to (b, c, e)); in (l) = 5 μm (valid for (k)).