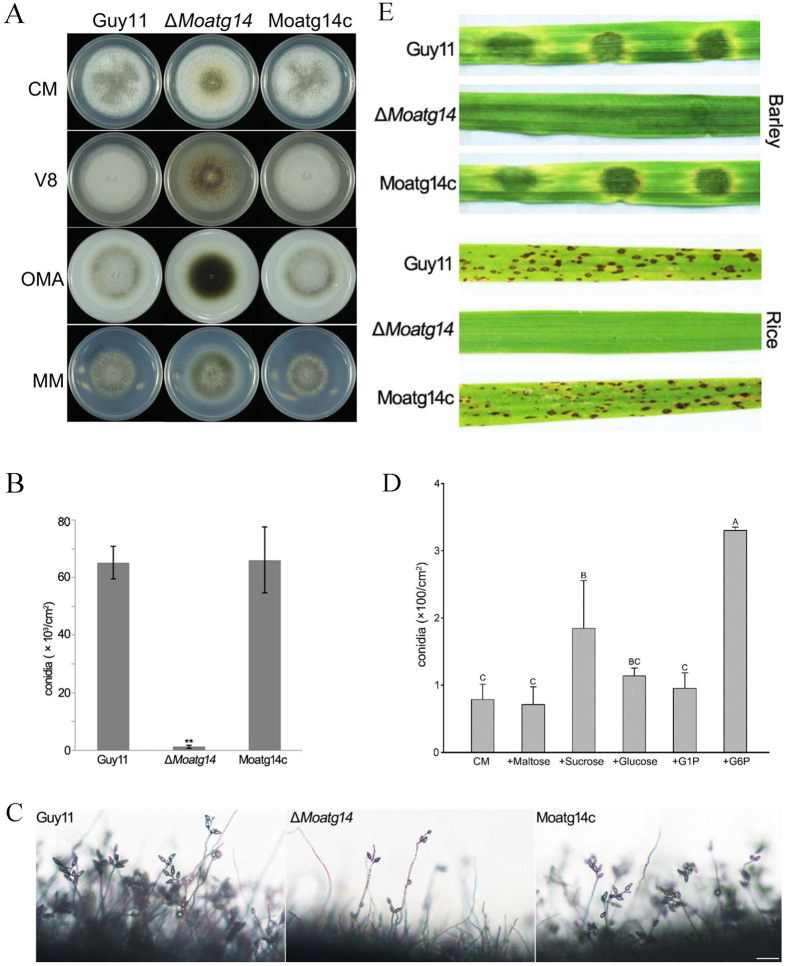
Figure 3. Characteristics of M. oryzae strains.
(A) Guy11, the ΔMoatg14 mutant, and the complemented strain Moatg14c were grown on CM, V8, OMA, and MM medium for 8 days. (B) Few conidia were produced by the ΔMoatg14 mutant, in contrast to Guy11 and Moatg14c. Error bars represent one standard deviation (P < 0.01). Different letters indicate a significant difference in the conidiation of the ΔMoatg14 mutant, Guy11, and Moatg14c. (C) Development of conidia on conidiophores observed under cover slips with a light microscope 24 h after induction of conidiation. Few conidia developed in the ΔMoatg14 mutant. Scale bar = 50 μm. (D) Conidiation in the ΔMoatg14 mutant grown on CM medium and CM medium supplemented with 10 g/L maltose, 6.25 g/L sucrose, 10 g/L glucose, 1 mM G1P and 0.5 mM G6P. Error bars represent one standard deviation (P < 0.01). Different letters indicate a significant difference. (E) The MoAtg14 deletion mutant is nonpathogenic. Disease symptoms on cut leaves of barley inoculated with mycelial plugs from Guy11, the ΔMoatg14 mutant, and Moatg14c. Typical leaves were photographed 4 days after inoculation. Two-week-old rice seedlings were inoculated by spraying with 1 × 105 conidia/ml conidia suspensions from Guy11, the ΔMoatg14 mutant, and Moatg14c. Lesion formation on the rice leaves was evaluated 7 days after inoculation.