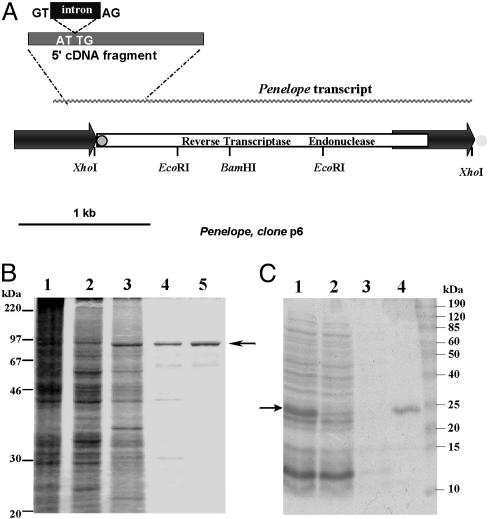
Fig. 1.
Structure of Penelope and purification of its ORF-encoded activities. (A) The transpositionally active p6 Penelope copy (12). The 5′ fragment of cDNA with the splice donor/acceptor sites for the 75-bp intron is shown above the diagram. The position of the 34-bp tail in the 5′ terminal part of Penelope is shown by a gray circle outlined in black, and its position at the 3′ ends of other copies of Penelope (but not p6) is shown by a gray circle with no outline. (B) Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of protein extracts from S. frugiperda cells infected by BacPenORF at different stages of multistep chromatography: 1, crude extract; 2, phosphocellulose P11; 3, heparin-Sepharose; 4, Mono S; and 5, 50-kDa Centricon. (C) Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of His6-tagged Penelope EN after purification by metal-chelate chromatography: 1, IPTG-induced E. coli lysate; 2, flowthrough after Ni-NTA column; 3, wash with 50 mM imidazole; and 4, elution with 250 mM imidazole. Arrows indicate the position of 93-kDa (B) and 22.4-kDa (C) proteins.