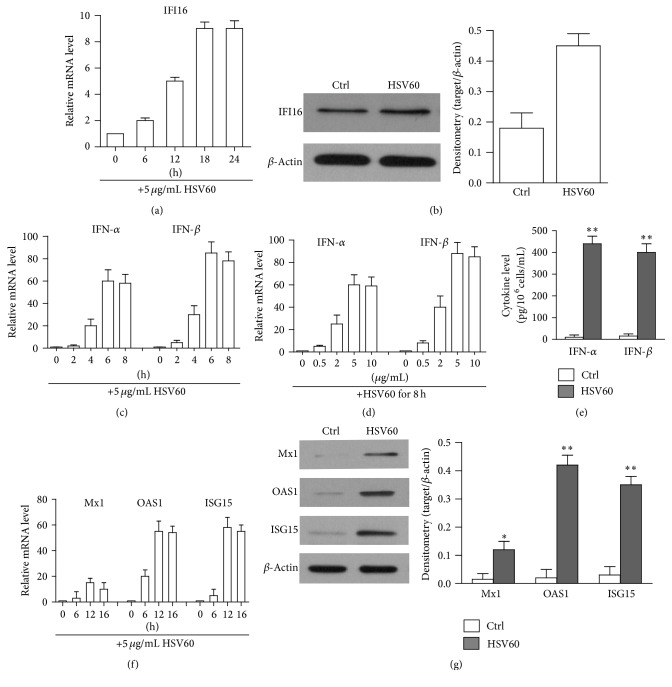
Figure 4.
HSV60-induced immune responses. (a) Upregulation of IFI16. hAD-MSCs were stimulated with 5 μg/mL HSV60 at indicated time points. Relative mRNA levels of IFI16 were determined by real-time PCR. (b) The protein levels of IFI16 were determined by Western blot. hAD-MSCs were lysed 24 h after HSV60 stimulation. β-Actin was used as loading control. (c) Time-dependent IFN-α and IFN-β expression. Total mRNA was extracted from hAD-MSCs at the indicated time points post HSV60 stimulation. Relative mRNA levels of IFN-α and IFN-β were determined using real-time PCR by normalizing to β-actin. (d) Dose-dependent IFN-α and IFN-β expression. hAD-MSCs were stimulated with indicated dose of HSV60 for 6 h. Relative mRNA levels of IFN-α and IFN-β were determined by real-time PCR. (e) IFN-α and IFN-β secretion. hAD-MSCs were stimulated with HSV60. After 24 h, IFN-α and IFN-β levels in culture medium were measured using ELISA. (f) Expression of antiviral proteins in mRNA levels after HSV60 stimulation. Total RNA was extracted from hAD-MSCs at the different times points after stimulation with HSV60. Relative mRNA levels of ISG15, OAS1, and Mx1 were determined using real-time PCR. (g) Expression of antiviral proteins in protein levels. hAD-MSCs were stimulated with HSV60. After 24 h, the cell lysates were extracted to Western blot to probe antiviral proteins. The cells treated with LyoVec alone served as Ctrl. Western blot images represent at least three experiments. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of three experiments. ∗ P < 0.05; ∗∗ P < 0.01.