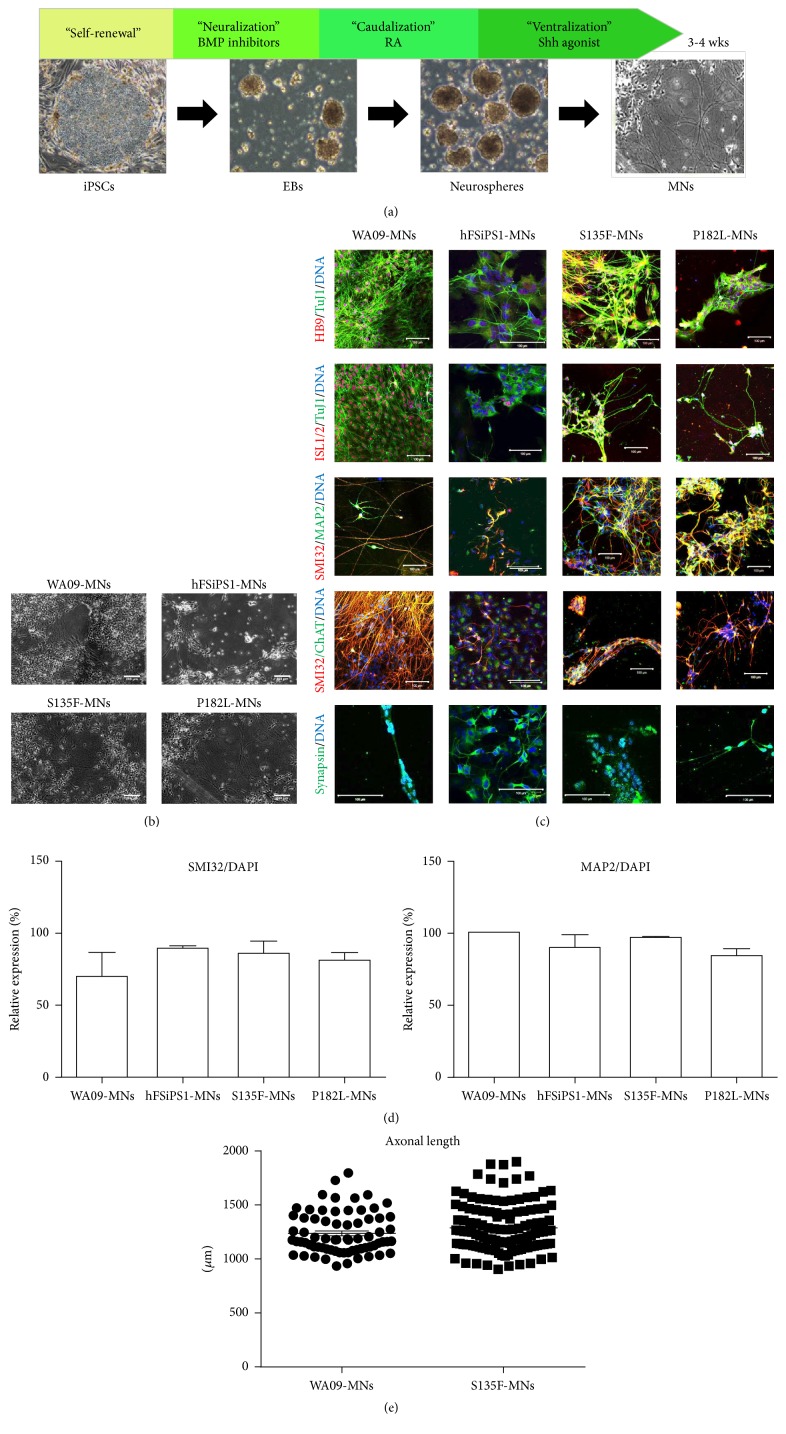
Figure 2.
Generation of CMT2F-specific in vitro model by differentiation of patient-derived iPSCs into MNs. (a) Schematic presentation of MN differentiation. (b) Differentiated MNs showed typical cellular morphology (original magnification, 50x). Scale bars: 200 μm. (c) S135F-MNs and P182L-MNs expressed MN-specific transcription factors such as HB9 and ISL1/2; neuronal cytoskeletal markers such as TuJ1, SMI32, and MAP2; ChAT; and the synaptic vesicular marker synapsin (original magnification, 400x and 600x). Scale bars: 100 μm. (d) Differentiation efficiency of S135F-MNs and P182L-MNs was comparable to control MNs in terms of neuronal marker expression such as SMI32/DAPI and MAP2/DAPI (WA09-MNs; N = 30, hFSiPS1-MNs; N = 329, S135F-MNs; N = 1730, and P182L-MNs; N = 1090). (e) Axonal length of S135F-MNs was comparable to that of control MNs. Axonal length was measured by culturing fully differentiated MNs in microchannel plates for an additional 2 weeks (WA09-MNs: N = 70 and S135F-MNs: N = 121).