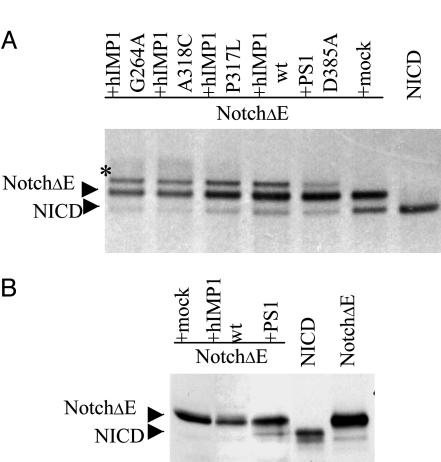
Fig. 2.
Expression of human IMP1 in mammalian cells and S3 cleavage of Notch1 receptor. (A) Overexpression of hIMP1wt or mutant forms does not facilitate cleavage of Notch1 as detected by pulse-chase analysis. HEK293 cells were cotransfected with the constructs (i) NotchΔE and (ii) wild or mutant hIMP1 or PS1 D385A or mock (pcLacZ). NotchΔE and NOTCH1 intracellular domain (NICD) (predicted derivate of NotchΔ S3-cleavage) are fused to c-myc epitope. Cells were pulse-labeled and chased for 60 min. Protein extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-c-myc antibodies and subjected to electrophoresis and autoradiography. As described, the NICD product of S3 cleavage is clearly detected in 60 min of pulse-chase in HEK293 cells expressing membrane-tethering NotchΔE. The coexpression of NotchΔE with loss-of-function PS1 D385A mutant has dominant-negative effect suppressing S3 activity of endogenous PS. The hIMP1wt or the hIMP1 mutant isoforms (G264A, A318C, and P317L) do not increase, but reduce efficiency of S3-cleavage. The modified Notch1 fragment observed in cells overexpressing IMP1 constructs is designated by asterisk. (B) Expression of hIMP1 in PS1-/-,PS2-/- fibroblasts does not induce NotchΔE cleavage, unlike expression of exogenous PS1. Notch1 C-terminal fragments are detected by Western blot analysis with c-myc AB (Supporting information).